
-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
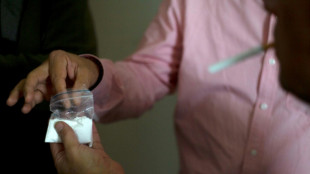 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
-
Artist rubs out Meloni church fresco after controversy

-
 Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
-
US removing 700 immigration officers from Minnesota

-
 Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
-
Coach Thioune tasked with saving battling Bremen

-
 Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
-
Son of Norway's crown princess admits excesses but denies rape

-
 US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
-
Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'

-
 'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer

-
 Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
-
Stocks stabilise after Wall St AI-fuelled sell-off

-
 Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
-
Netflix film probes conviction of UK baby killer nurse

-
 Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
Timber hopes League Cup can be catalyst for Arsenal success
-
China calls EU 'discriminatory' over probe into energy giant Goldwind

-
 Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
Sales warning slams Ozempic maker Novo Nordisk's stock
-
Can Vonn defy ACL rupture to win Olympic medal?

-
 Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
Breakthrough or prelude to attack? What we know about Iran-US talks
-
German far-right MP detained over alleged Belarus sanctions breach


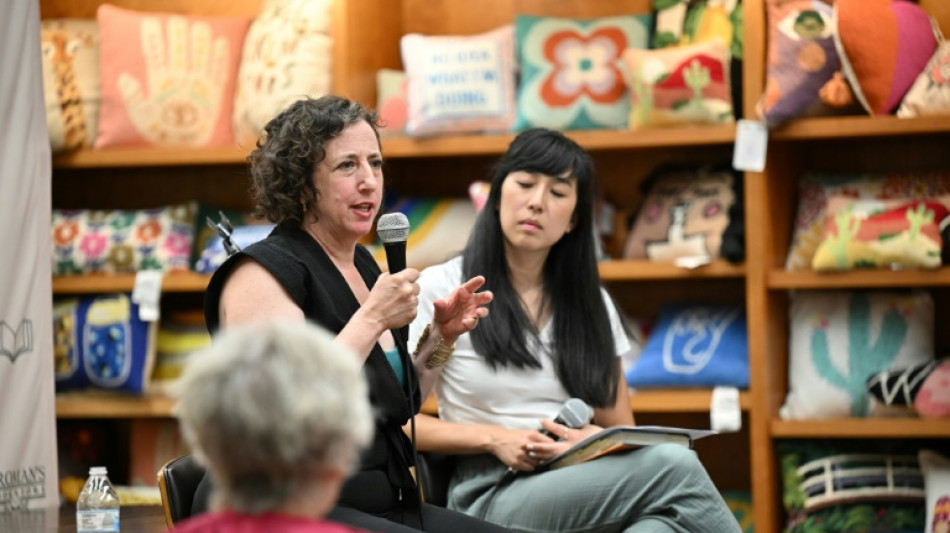
The US towns that took on 'forever chemical' giants -- and won
No corner of Earth is untouched. From Tibet to Antarctica, so-called "forever chemicals" have seeped into the blood of nearly every living creature.
Tainting food, water and wildlife, these toxic substances have been linked to ailments ranging from birth defects to rare cancers.
Yet if it weren't for the efforts of residents in two heavily impacted American towns, the world might still be in the dark.
In the new book "They Poisoned the World: Life and Death in the Age of Chemicals," investigative journalist Mariah Blake recounts how people in Parkersburg, West Virginia, and Hoosick Falls, New York, blew the whistle on the industrial giants that poisoned them -- and, in the process, forced the world to reckon with per‑ and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS.
"We're talking about a class of chemicals that doesn't break down in the environment," Blake tells AFP, calling it the "worst contamination crisis in human history."
First developed in the 1930s, PFAS are prized for their strength, heat resistance, and water- and grease-repelling powers. Built on the carbon-fluoride bond -- the strongest in chemistry -- they persist like radioactive waste and accumulate in our bodies, hence the "forever" nickname.
Blake's research traces their history, from accidental discovery by a DuPont chemist to modern usage in cookware, clothing, and cosmetics.
They might have remained a curiosity if Manhattan Project scientists hadn't needed a coating that could withstand atomic-bomb chemistry, helping companies produce them at scale.
- Corporate malfeasance -
Industry knew the risks early. Internal tests showed plant workers suffered chemical burns and respiratory distress. Crops withered and livestock died near manufacturing sites.
So how did they get away with it? Blake tracks the roots to the 1920s, when reports emerged that leaded gasoline caused psychosis and death among factory workers. In response, an industry-backed scientist advanced a now-infamous doctrine: chemicals should be presumed safe until proven harmful.
This "Kehoe principle" incentivized corporations to manufacture doubt around health risks -- a big reason it took until last year for the US to finalize a ban on asbestos.
DuPont's own studies warned that Teflon had no place on cookware. But after a French engineer coated his wife's muffin tins with it, a Parisian craze took off -- and an American entrepreneur sold the idea back to DuPont.
Soon nonstick pans were flying off shelves, thanks in part to a regulatory gap: PFAS, along with thousands of other chemicals, were "grandfathered" into the 1976 Toxic Substances Control Act and required no further testing.
- Massive litigation -
The cover-up began to unravel in the 1990s in Parkersburg, where DuPont had for decades been dumping Teflon waste into pits and the Ohio River.
The town reaped economic benefits, but female plant workers were having babies with birth defects, a cattle farmer downstream was losing his herd, and residents developed rare cancers.
Blake tells the story through "accidental activists." One is Michael Hickey, a preppy insurance underwriter with no interest in politics or the environment. After cancer took his father and friends, he started testing Hoosick Falls's water.
Another is Emily Marpe, "a teen mom with a high school education" who saved to buy her family's dream house in upstate New York, only to learn the water flowing from the taps was fouled with PFAS that now coursed through their blood in massive levels.
"She knew the science inside out," says Blake, "and became an incredibly articulate advocate."
Years of litigation yielded hundreds of millions in settlements and forced DuPont and 3M to phase out two notorious PFAS. But the companies pivoted to substitutes like GenX -- later shown to be just as toxic.
Still, Blake argues the tide is turning. France has banned PFAS in many consumer goods, the EU is considering a ban, and in the US, states are moving to restrict PFAS in sludge fertilizer and food packaging.
Liabilities linked to the chemicals are driving major retailers from McDonald's to REI to pledge PFAS-free products.
Her optimism is tempered by the political climate. Just this week, the Trump administration announced the rollback of federal drinking water standards for four next-generation PFAS chemicals.
But she believes the momentum is real.
"Ordinary citizens who set out to protect their families and communities have really created this dramatic change," she says. "It's like climate change -- it feels intractable, but here's a case where people have made major headway."
U.Shaheen--SF-PST


