
-
 The Cupra Raval will be launched in 2026
The Cupra Raval will be launched in 2026
-
New id.Polo comes electric

-
 Iran defies US threats to insist on right to enrich uranium
Iran defies US threats to insist on right to enrich uranium
-
Seifert powers New Zealand to their record T20 World Cup chase

-
 Naib's fifty lifts Afghanistan to 182-6 against New Zealand
Naib's fifty lifts Afghanistan to 182-6 against New Zealand
-
Paul Thomas Anderson wins top director prize for 'One Battle After Another'

-
 De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums
De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums
-
NFL embraces fashion as league seeks new audiences

-
 What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?
What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?
-
Real Madrid can wait - Siraj's dream night after late T20 call-up

-
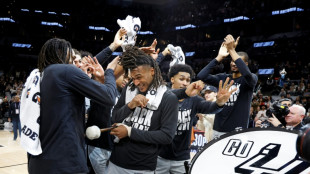 Castle's monster night fuels Spurs, Rockets rally to beat Thunder
Castle's monster night fuels Spurs, Rockets rally to beat Thunder
-
Japan votes in snow-hit snap polls as Takaichi eyes strong mandate

-
 Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents
Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents
-
Berlin's crumbling 'Russian houses' trapped in bureaucratic limbo

-
 Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya
Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya
-
Super Bowl set for Patriots-Seahawks showdown as politics swirl

-
 Sengun shines as Rockets rally to beat NBA champion Thunder
Sengun shines as Rockets rally to beat NBA champion Thunder
-
Matsuyama grabs PGA Phoenix Open lead with Hisatsune one back

-
 Washington Post CEO out after sweeping job cuts
Washington Post CEO out after sweeping job cuts
-
Haiti's transitional council hands power to PM

-
 N. Korea to hold party congress in February, first since 2021
N. Korea to hold party congress in February, first since 2021
-
Thailand votes after three leaders in two years

-
 Swiss joy as Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics
Swiss joy as Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics
-
George backs England to 'kick on' after Six Nations rout of Wales

-
 Malinin upstaged as Japan keep pressure on USA in skating team event
Malinin upstaged as Japan keep pressure on USA in skating team event
-
Japan's Kimura soars to Olympic gold in snowboard big air final

-
 Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow
Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow
-
Veteran French politician loses culture post over Epstein links

-
 Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold
Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold
-
Arteta backs confident Gyokeres to hit 'highest level'

-
 Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa
Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa
-
England's Arundell 'frustrated' despite hat-trick in Wales romp

-
 Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday
-
Arundell hat-trick inspires England thrashing of Wales in Six Nations opener

-
 Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
-
Rosenior hails 'unstoppable' Palmer after treble tames Wolves

-
 French ex-minister offers resignation from Paris cultural hub over Epstein links
French ex-minister offers resignation from Paris cultural hub over Epstein links
-
New NBA dunk contest champ assured and shooting stars return

-
 Shiffrin says will use lessons learnt from Beijing flop at 2026 Games
Shiffrin says will use lessons learnt from Beijing flop at 2026 Games
-
Takaichi tipped for big win as Japan votes

-
 Lens return top of Ligue 1 with win over Rennes
Lens return top of Ligue 1 with win over Rennes
-
Shiffrin learning from Beijing lessons ahead of Milan-Cortina bow

-
 Demonstrators in Berlin call for fall of Iran's Islamic republic
Demonstrators in Berlin call for fall of Iran's Islamic republic
-
'Free the mountains!": clashes at Milan protest over Winter Olympics

-
 Townsend accepts pressure will mount on him after Italy defeat
Townsend accepts pressure will mount on him after Italy defeat
-
BMW iX3 new style and design

-
 Suryakumar's 84 leads India to opening win over USA in T20 World Cup
Suryakumar's 84 leads India to opening win over USA in T20 World Cup
-
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Milan-Cortina Games

-
 Barca beat Mallorca to extend Liga lead
Barca beat Mallorca to extend Liga lead
-
Gyokeres lifts Arsenal nine clear as Man Utd pile pressure on Frank


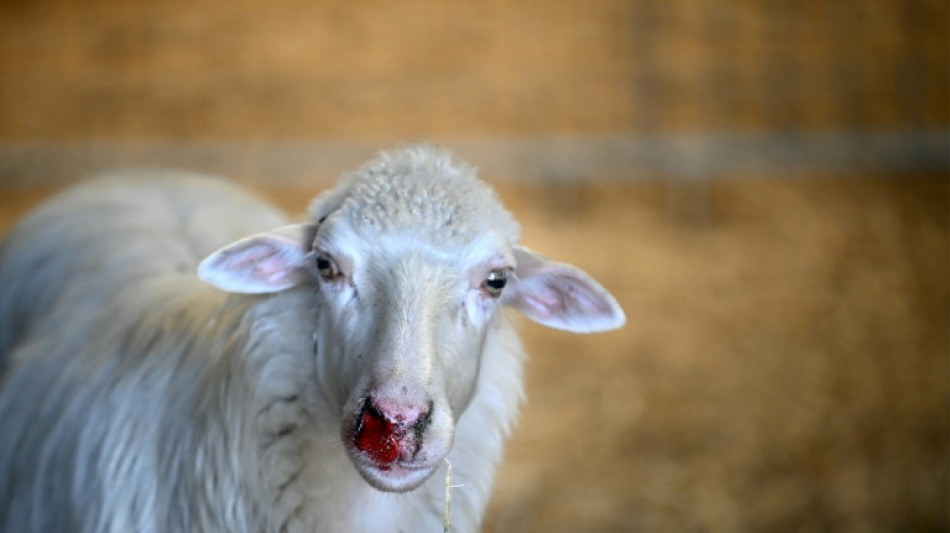
Sardinia's sheep farmers battle bluetongue as climate warms
The sheep huddle together, bleeding from the nose, aborting lambs or suffocating on saliva as they succumb to bluetongue, a virus sweeping through flocks on the Italian island of Sardinia.
Some 20,000 sheep have died so far this year on the island, which is home to nearly half Italy's flock and plays an important role in the production of famed Italian cheeses such as Pecorino.
It is another blow for farmers in a region already battered by a drought aggravated by man-made climate change -- which experts say is also fuelling the spread of bluetongue and longer outbreaks.
"The virus hit about two and a half months earlier than usual," 39-year-old farmer Michela Dessi told AFP as she scanned her flock for panting or limping sheep in her fields in Arbus in western Sardinia.
Bluetongue does not present any risks to humans but in animals it causes swollen heads, high fevers, mouth ulcers, difficulty swallowing and breathing, and can turn an infected animal's tongue blue.
It is transmitted between animals by biting midges.
While cattle, goats and deer can get it too, sheep are the most severely affected, according to the World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH).
Infected and pregnant ewes abort or their lambs are born deformed, and survivors can lose their wool.
Sunken sides are a sign the ewes are carrying dead foetuses. The sick animals struggle to expel them.
- Virus peaks -
The infection rate this year on Dessi's farm is about 60 percent, and some 30 percent of her sheep have aborted.
Around 50 of her 650 sheep have died -- and in a way she said was "horrible to watch".
With high fevers, "they refuse food and water and some suffocate or drown in their own saliva", she said, adding that it is illegal to euthanise them.
Nearly 3,000 outbreaks have been recorded so far this year in Sardinia, compared to 371 last year -- and the end is not yet in sight.
Bluetongue used to peak in Sardinia in August but has done so as late as November in recent years, according to the region's veterinary research institute (IZS).
"Climatic conditions heavily influence midge populations," the animal health division at the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization in Rome told AFP.
They affect "their biting behaviour and the speed of development of the virus, with climate change likely driving the virus's expansion... and contributing to larger outbreaks".
Cases have been reported this year in other European countries, from neighbouring France to Portugal, Spain, Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands.
Bluetongue has been present in Sardinia since 2000 but Italy's farming lobby Coldiretti says authorities are too slow each year to vaccinate the island's flocks.
The costs of failing to rein it in are high.
A University of Bologna study last year found the 2017 outbreak, which killed 34,500 sheep, cost an estimated 30 million euros ($33 million).
That included damages suffered by farms -- deaths, reduced milk yields, infertility, abortions -- costs to animal health authorities and subventions paid by the region to affected farms.
- Mass graves -
"The first outbreaks occur in the same at-risk areas each year," meaning highly targeted measures could theoretically prevent outbreaks, said Stefano Cappai from research institute IZS.
There are three variants on the island this year, two of which can be vaccinated against, with mortality rates twice as high among unvaccinated sheep.
Flocks should be vaccinated in March or April, Cappai said, but vaccines were only issued by the region in mid-June this year.
By that point, the virus had begun to spread unchecked.
Even if the vaccines had been made available earlier, some farmers fear to use them.
Others only vaccinate part of their flock, which means they fail to reach herd immunity, Cappai said.
And some farmers -- like Dessi -- vaccinated her flock, only for the sheep to catch the variant for which there is no vaccine yet.
Battista Cualbu, head of Coldiretti in Sardinia, who also has an outbreak on his farm, said vaccines are not enough and authorities must disinfect areas and provide midge repellents.
"It would certainly save public money because the region has to pay compensation for dead livestock (and) lost income," he said, including less milk sold and fewer lambs for the slaughterhouse.
Compensation is set at 150 euros per sheep killed by bluetongue -- a figure Coldiretti is battling to increase, although the region has failed to pay up over the past three years, Dessi said.
As temperatures fall, the case numbers are expected to decline but Dessi said the end was weeks away.
"I've dug three mass graves already and I fear the worst is still to come", she said.
H.Jarrar--SF-PST




