
-
 Sengun shines as Rockets rally to beat NBA champion Thunder
Sengun shines as Rockets rally to beat NBA champion Thunder
-
Matsuyama grabs PGA Phoenix Open lead with Hisatsune one back

-
 Washington Post CEO out after sweeping job cuts
Washington Post CEO out after sweeping job cuts
-
Haiti's transitional council hands power to PM

-
 N. Korea to hold party congress in February, first since 2021
N. Korea to hold party congress in February, first since 2021
-
Thailand votes after three leaders in two years

-
 Swiss joy as Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics
Swiss joy as Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics
-
George backs England to 'kick on' after Six Nations rout of Wales

-
 Malinin upstaged as Japan keep pressure on USA in skating team event
Malinin upstaged as Japan keep pressure on USA in skating team event
-
Japan's Kimura soars to Olympic gold in snowboard big air final

-
 Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow
Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow
-
Veteran French politician loses culture post over Epstein links

-
 Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold
Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold
-
Arteta backs confident Gyokeres to hit 'highest level'

-
 Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa
Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa
-
England's Arundell 'frustrated' despite hat-trick in Wales romp

-
 Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday
-
Arundell hat-trick inspires England thrashing of Wales in Six Nations opener

-
 Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
-
Rosenior hails 'unstoppable' Palmer after treble tames Wolves

-
 French ex-minister offers resignation from Paris cultural hub over Epstein links
French ex-minister offers resignation from Paris cultural hub over Epstein links
-
New NBA dunk contest champ assured and shooting stars return

-
 Shiffrin says will use lessons learnt from Beijing flop at 2026 Games
Shiffrin says will use lessons learnt from Beijing flop at 2026 Games
-
Takaichi tipped for big win as Japan votes

-
 Lens return top of Ligue 1 with win over Rennes
Lens return top of Ligue 1 with win over Rennes
-
Shiffrin learning from Beijing lessons ahead of Milan-Cortina bow

-
 Demonstrators in Berlin call for fall of Iran's Islamic republic
Demonstrators in Berlin call for fall of Iran's Islamic republic
-
'Free the mountains!": clashes at Milan protest over Winter Olympics

-
 Townsend accepts pressure will mount on him after Italy defeat
Townsend accepts pressure will mount on him after Italy defeat
-
BMW iX3 new style and design

-
 Suryakumar's 84 leads India to opening win over USA in T20 World Cup
Suryakumar's 84 leads India to opening win over USA in T20 World Cup
-
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Milan-Cortina Games

-
 Barca beat Mallorca to extend Liga lead
Barca beat Mallorca to extend Liga lead
-
Gyokeres lifts Arsenal nine clear as Man Utd pile pressure on Frank

-
 Late Guirassy winner for Dortmund trims Bayern's lead atop Bundesliga
Late Guirassy winner for Dortmund trims Bayern's lead atop Bundesliga
-
'Free the mountains!": protest in Milan over Winter Olympics
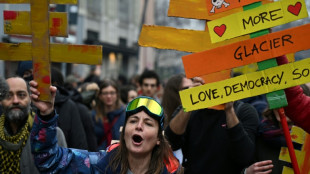
-
 Gyokeres double helps Arsenal stretch Premier League lead
Gyokeres double helps Arsenal stretch Premier League lead
-
New Skoda Epiq: modern with range

-
 Six Nations misery for Townsend as Italy beat sorry Scotland
Six Nations misery for Townsend as Italy beat sorry Scotland
-
Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain

-
 Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection
Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection
-
Over 2,200 IS detainees transferred to Iraq from Syria: Iraqi official

-
 Norway's Ruud tops Olympic men's freeski slopestyle qualifying
Norway's Ruud tops Olympic men's freeski slopestyle qualifying
-
Czech qualifier Bejlek claims first title in Abu Dhabi

-
 French duo reach Shanghai, completing year-and-a-half walk
French duo reach Shanghai, completing year-and-a-half walk
-
Australian snowboarder James eyes elusive Olympic gold

-
 Sequins and snow: Eva Adamczykova makes Olympic return
Sequins and snow: Eva Adamczykova makes Olympic return
-
Vonn set for Olympic medal bid after successful downhill training

-
 Shepherd takes hat-trick as West Indies beat Scotland in T20 World Cup
Shepherd takes hat-trick as West Indies beat Scotland in T20 World Cup
-
Sausages will sell after thrill-seeker Von Allmen wins Olympic downhill


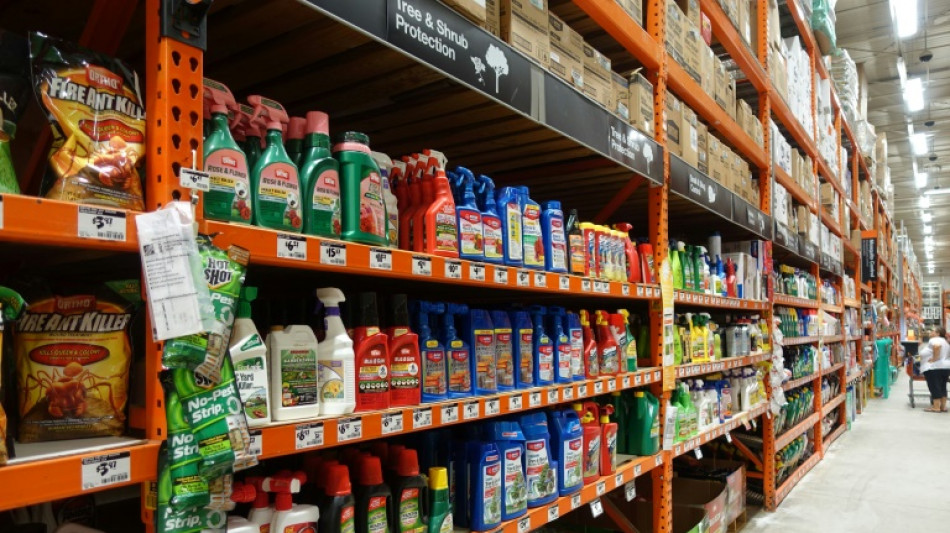
'Truly frightening': Pesticides increasingly laced with forever chemicals
Toxic "forever chemicals" are increasingly being used in US pesticides, threatening human health as they contaminate waterways and are sprayed on staple foods, a study said Wednesday.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have come under increasing scrutiny in recent years, but environmental regulations against them have mainly paid attention to sources such as industrial facilities, landfills and consumer products like certain cookware and paints.
New research published in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Health Perspectives says that pesticides used on crops including corn, wheat, spinach, apples and strawberries -- and other sources such as insect sprays and pet flea treatment -- can now be added to the list.
"The more we look, the more we find it," co-author Alexis Temkin, a toxicologist at the nonprofit Environmental Working Group, told AFP.
"And it just emphasizes the importance of cutting down on sources and really regulating these chemicals."
Research suggests that high levels of exposure to forever chemicals weakens human immune systems, making them less responsive to vaccines and more susceptible to infections.
There is also emerging evidence they may reduce fertility, lead to growth delays in children, and interfere in the body's natural hormones.
For the new paper, the authors trawled public databases and carried out freedom of information requests to obtain information on both "active" and "inert" ingredients in pesticides.
Active ingredients are those that target pests, while those that are called inert are everything else. The latter are not required to be disclosed on the label even though they can increase the efficacy and persistence of the toxic active ingredient, and can be toxic themselves.
The researchers uncovered a concerning trend: 14 percent of all US pesticide active ingredients are PFAS, including nearly one-third of active ingredients approved in the past decade.
Eight approved inert ingredients in pesticides were PFAS, including the non-stick chemical known by the brand name Teflon.
The Teflon company that made nonstick pans with this chemical ended its use in 2013, and its elimination was tied in research to fewer low birth weight babies. In February, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced plans to ban its use in pesticides.
Study co-author David Andrews, a scientist at the nonprofit Environmental Working Group, told AFP that part of the problem stemmed from a narrower definition of PFAS molecules by the EPA compared to that adopted by the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
Adding PFAS to pesticides makes them more powerful and longer lasting, Andrews told AFP, which could be another driving factor.
Forever chemicals were first developed in the 1940s and have now accumulated in the environment globally, entering the air, soil, groundwater, lakes and rivers.
More than 15,000 synthetic chemicals qualify as PFAS, and their indestructibility arises from their carbon-fluorine bonds, one of the strongest types of bonds in organic chemistry.
- 'Ineffective regulation' -
Another critical issue identified by the study was the plastic containers used to store pesticides and fertilizers, 20-30 percent of which are "fluorinated" to improve their strength, but can leach PFAS back into the container's contents.
Such unintentional addition of extra PFAS back into the pesticide has been found during testing, and although the EPA moved to ban fluoridation of these containers, its decision was overturned by a US court.
"This is truly frightening news, because pesticides are some of the most widely dispersed pollutants in the world," co-author Nathan Donley, environmental health science director at the Center for Biological Diversity, said about the findings.
"Lacing pesticides with forever chemicals is likely burdening the next generation with more chronic diseases and impossible cleanup responsibilities."
The authors recommended measures including a ban on fluorinated plastic containers, mandating disclosure of all "inert" ingredients on product labels, comprehensive study of what happens to pesticide compounds in the environment, and more research on their effects on humans.
"The regulations surrounding pesticides are currently outdated and ineffective," scientists at Emory University wrote in a related commentary, calling on the EPA to get a better grasp on the rising threat.
A.AbuSaada--SF-PST




