
-
 Pistons end Knicks' NBA winning streak, Celtics edge Heat
Pistons end Knicks' NBA winning streak, Celtics edge Heat
-
Funerals for victims of suicide blast at Islamabad mosque that killed at least 31

-
 A tale of two villages: Cambodians lament Thailand's border gains
A tale of two villages: Cambodians lament Thailand's border gains
-
Police identify suspect in disappearance of Australian boy

-
 Cuba adopts urgent measures to address energy crisis: minister
Cuba adopts urgent measures to address energy crisis: minister
-
Not-so-American football: the Super Bowl's overseas stars

-
 Trump says US talks with Iran 'very good,' more negotiations expected
Trump says US talks with Iran 'very good,' more negotiations expected
-
Trump administration re-approves twice-banned pesticide

-
 Hisatsune leads Matsuyama at Phoenix Open as Scheffler makes cut
Hisatsune leads Matsuyama at Phoenix Open as Scheffler makes cut
-
Beyond the QBs: 5 Super Bowl players to watch

-
 Grass v artificial turf: Super Bowl players speak out
Grass v artificial turf: Super Bowl players speak out
-
Police warn Sydney protesters ahead of Israeli president's visit

-
 Bolivia wants closer US ties, without alienating China: minister
Bolivia wants closer US ties, without alienating China: minister
-
Ex-MLB outfielder Puig guilty in federal sports betting case

-
 Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with dazzling ceremony
Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with dazzling ceremony
-
China overturns death sentence for Canadian in drug case

-
 Trump reinstates commercial fishing in protected Atlantic waters
Trump reinstates commercial fishing in protected Atlantic waters
-
Man Utd can't rush manager choice: Carrick

-
 Leeds boost survival bid with win over relegation rivals Forest
Leeds boost survival bid with win over relegation rivals Forest
-
Stars, Clydesdales and an AI beef jostle for Super Bowl ad glory

-
 Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
-
Freeski star Gu says injuries hit confidence as she targets Olympic treble

-
 UK police search properties in Mandelson probe
UK police search properties in Mandelson probe
-
Bompastor extends contract as Chelsea Women's boss despite slump

-
 Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with glittering ceremony
Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with glittering ceremony
-
A French yoga teacher's 'hell' in a Venezuelan jail

-
 England's Underhill taking nothing for granted against Wales
England's Underhill taking nothing for granted against Wales
-
Fans cheer for absent Ronaldo as Saudi row deepens

-
 Violence-ridden Haiti in limbo as transitional council wraps up
Violence-ridden Haiti in limbo as transitional council wraps up
-
Hundreds protest in Milan ahead of Winter Olympics

-
 Suspect in murder of Colombian footballer Escobar killed in Mexico
Suspect in murder of Colombian footballer Escobar killed in Mexico
-
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS Minnesota United

-
 Wainwright says England game still 'huge occasion' despite Welsh woes
Wainwright says England game still 'huge occasion' despite Welsh woes
-
WADA shrugs off USA withholding dues

-
 France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron
-
Winter Olympics to open with star-studded ceremony

-
 Trump posts, then deletes, racist clip of Obamas as monkeys
Trump posts, then deletes, racist clip of Obamas as monkeys
-
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe

-
 Trump deletes racist video post of Obamas as monkeys
Trump deletes racist video post of Obamas as monkeys
-
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS side Minnesota United

-
 UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties
UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties
-
Russian drone hits Ukrainian animal shelter

-
 US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests
US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests
-
French cycling hope Seixas dreaming of Tour de France debut

-
 France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source
-
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles

-
 Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque
Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque
-
Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman

-
 US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested
US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested
-
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise

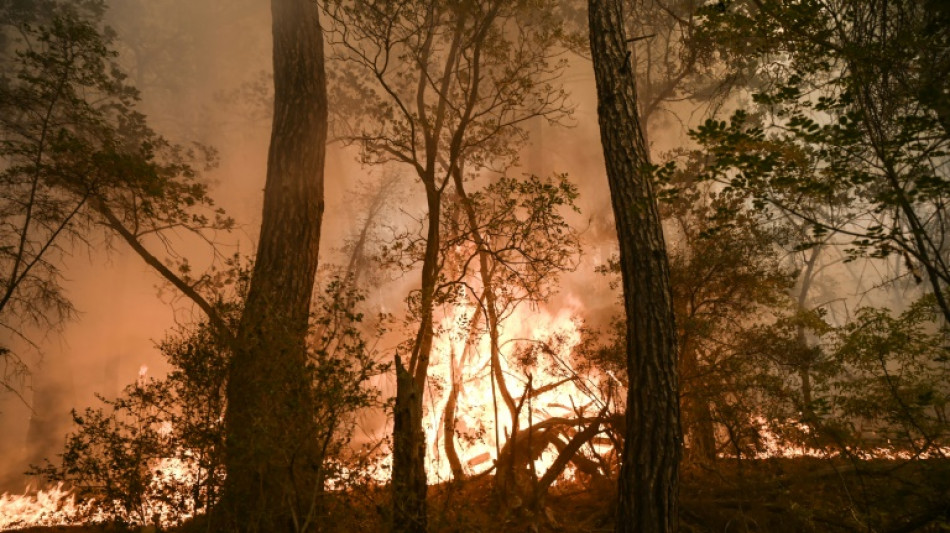
Forest fires: a record year
As the deadliest year this century for forest fires comes to a close, attention is turning to how to prevent such infernos happening again.
In 2023 forest fires destroyed nearly 400 million hectares (988 million acres) of land around the world, killed more than 250 people and emitted 6.5 billion tonnes of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide.
Pauline Vilain-Carlotti, a researcher in geography and wildfires, told AFP 2023's fires had been "out of control" and showed that firefighting capacities were inadequate. Efforts should now be focussed on prevention rather than cure.
"We are no longer capable of coping under current conditions with the current firefighting manpower, thus the importance of acting beforehand on prevention, rather than afterwards on firefighting and extinguishing," she said.
- Historic fires in Canada -
Records tumbled on the American continent this year as it went through a forest fire season in which nearly 80 million hectares (198 million acres) had burned by December 23.
That is one and a half times the surface area of Spain, and 10 million hectares (24 million acres) more than the average from 2012-2022 on the same date, according to the Global Wildfire Information System (GWIS).
Canada, where 18 million hectares (44.5 million acres) went up in smoke over the year, drove the increase.
The fires were caused by dryer and hotter weather conditions driven by climate change.
- Deadly year -
With 97 dead and 31 missing in fires in Hawaii in August, 34 killed in Algeria, and at least 26 dead in Greece, the year with more than 250 deaths overall was the deadliest of the 21st century, according to the Emergency Events Database (EM-DAT) run by the Catholic University of Louvain in Belgium.
Vilain-Carlotti told AFP the rate of excess deaths risks increasing in the coming years, as wildfires come dangerously close to towns and cities.
In 2023 the wildfires engulfed not only areas usually susceptible to forest fires like Greece, Italy, Tunisia, and Algeria in the Mediterranean basin and North America and Australia, but also areas which are usually spared like Hawaii or Tenerife.
In August, Hawaii's historic royal seat of Lahaina was levelled by a wildfire.
- Six billion tonnes of CO2 -
As the fires spread even further, vegetation has less time to regrow, leaving the forests liable to lose their capacity to absorb carbon dioxide.
According to recent studies, the fires reduce the storage of carbon dioxide by around 10 percent, Solene Turquety, a researcher at France's LATMOS (Atmospheres, Environments, Space Observations Laboratory), said.
And as they burn, the trees suddenly release all of the CO2 that they have stored.
Since the beginning of 2023, wildfires have released some 6.5 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide, according to GWIS.
That compares to 36.8 billion tonnes from fossil fuels like oil, gas and coal and cement.
As a rule, around 80 percent of carbon generated by the forest fires is then reabsorbed by the vegetation which grows again the next season.
The remaining 20 percent then builds up in the atmosphere, contributing the climate change.
- Immediate health impact -
Apart from CO2, fires release a string of dangerous particles, from carbon monoxide to ash, soot, and organic carbon.
"These emissions very heavily alter the air quality, over hundreds of kilometres (miles) in the case of the most intense fires," Turquety said.
She said there is "an immediate health impact" on top of "the destruction of ecosystems, property and infrastructure".
According to a study published in September in Nature, the populations of the poorest countries, in particular in central Africa, are by far more exposed to the air pollution caused by these fires than those in industrialised countries.
G.AbuHamad--SF-PST

