
-
 Pistons end Knicks' NBA winning streak, Celtics edge Heat
Pistons end Knicks' NBA winning streak, Celtics edge Heat
-
Funerals for victims of suicide blast at Islamabad mosque that killed at least 31

-
 A tale of two villages: Cambodians lament Thailand's border gains
A tale of two villages: Cambodians lament Thailand's border gains
-
Police identify suspect in disappearance of Australian boy

-
 Cuba adopts urgent measures to address energy crisis: minister
Cuba adopts urgent measures to address energy crisis: minister
-
Not-so-American football: the Super Bowl's overseas stars

-
 Trump says US talks with Iran 'very good,' more negotiations expected
Trump says US talks with Iran 'very good,' more negotiations expected
-
Trump administration re-approves twice-banned pesticide

-
 Hisatsune leads Matsuyama at Phoenix Open as Scheffler makes cut
Hisatsune leads Matsuyama at Phoenix Open as Scheffler makes cut
-
Beyond the QBs: 5 Super Bowl players to watch

-
 Grass v artificial turf: Super Bowl players speak out
Grass v artificial turf: Super Bowl players speak out
-
Police warn Sydney protesters ahead of Israeli president's visit

-
 Bolivia wants closer US ties, without alienating China: minister
Bolivia wants closer US ties, without alienating China: minister
-
Ex-MLB outfielder Puig guilty in federal sports betting case

-
 Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with dazzling ceremony
Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with dazzling ceremony
-
China overturns death sentence for Canadian in drug case

-
 Trump reinstates commercial fishing in protected Atlantic waters
Trump reinstates commercial fishing in protected Atlantic waters
-
Man Utd can't rush manager choice: Carrick

-
 Leeds boost survival bid with win over relegation rivals Forest
Leeds boost survival bid with win over relegation rivals Forest
-
Stars, Clydesdales and an AI beef jostle for Super Bowl ad glory

-
 Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
-
Freeski star Gu says injuries hit confidence as she targets Olympic treble

-
 UK police search properties in Mandelson probe
UK police search properties in Mandelson probe
-
Bompastor extends contract as Chelsea Women's boss despite slump

-
 Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with glittering ceremony
Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with glittering ceremony
-
A French yoga teacher's 'hell' in a Venezuelan jail

-
 England's Underhill taking nothing for granted against Wales
England's Underhill taking nothing for granted against Wales
-
Fans cheer for absent Ronaldo as Saudi row deepens

-
 Violence-ridden Haiti in limbo as transitional council wraps up
Violence-ridden Haiti in limbo as transitional council wraps up
-
Hundreds protest in Milan ahead of Winter Olympics

-
 Suspect in murder of Colombian footballer Escobar killed in Mexico
Suspect in murder of Colombian footballer Escobar killed in Mexico
-
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS Minnesota United

-
 Wainwright says England game still 'huge occasion' despite Welsh woes
Wainwright says England game still 'huge occasion' despite Welsh woes
-
WADA shrugs off USA withholding dues

-
 France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron
-
Winter Olympics to open with star-studded ceremony

-
 Trump posts, then deletes, racist clip of Obamas as monkeys
Trump posts, then deletes, racist clip of Obamas as monkeys
-
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe

-
 Trump deletes racist video post of Obamas as monkeys
Trump deletes racist video post of Obamas as monkeys
-
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS side Minnesota United

-
 UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties
UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties
-
Russian drone hits Ukrainian animal shelter

-
 US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests
US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests
-
French cycling hope Seixas dreaming of Tour de France debut

-
 France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source
-
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles

-
 Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque
Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque
-
Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman

-
 US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested
US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested
-
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise

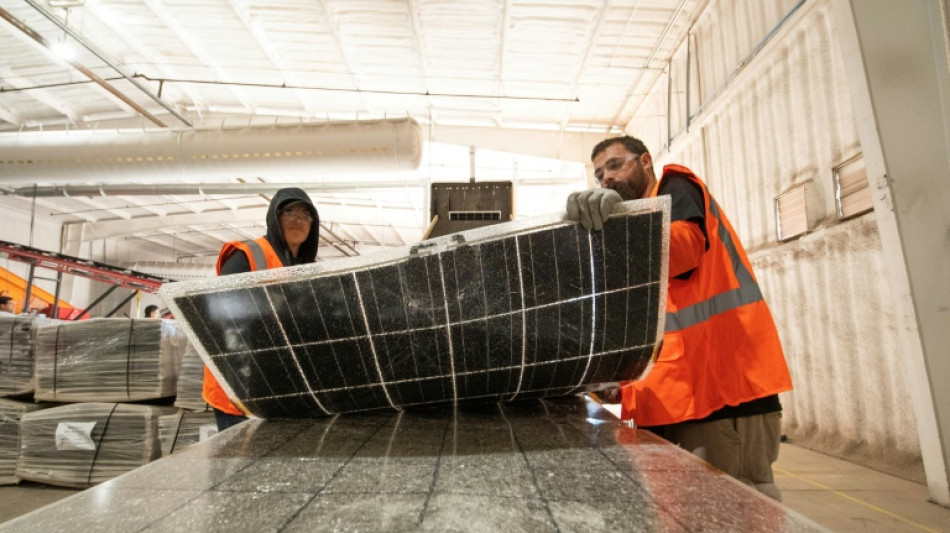
'Urban mining' offers green solution to old solar panels
As the world pivots from planet-warming fossil fuels to renewable energy, a new pollution problem is rearing its head: What to do with old or worn-out solar panels?
Thousands of photovoltaic slabs are being installed across the United States every day, particularly in the sunny west and south of the country, as states like California race to towards greener energy production.
But with an expected lifespan of around 30 years, the first wave of solar installations is now coming to the end of its usefulness, sparking a rush to recycle things that might otherwise end up in the landfill.
"What is about to happen is a tsunami of solar panels coming back into the supply chain," said Adam Saghei, chief executive of Arizona-based We Recycle Solar.
"One of the challenges with any industry is, there hasn't been that much planning for a circular economy.
"(Solar) is a sustainable form of energy; there needs to be a plan for the retirement of those assets."
Saghei's plan involves, among other things, reusing panels.
Anywhere up to five percent of panels either have a minor production defect or get damaged during transport or installation.
These still-working panels can be refurbished and diverted to other markets, often abroad, Saghei says.
But for the panels that no longer function -- either because they're decrepit, or because they were damaged beyond use during installation, or smashed by hailstones -- there's treasure to be found.
"We're doing what's called urban mining," says Saghei, refering to a process that took his engineers three years to perfect.
That mining recovers silver, copper, aluminium, glass and silicone -- all commodities that have a value on the open market.
While the uses for the metals might be obvious, what to do with silicone and glass is less so, but nonetheles intriguing.
"You can use it for sand traps on golf courses, you can refine it for sandblast mix, you can also use it for the stones or the glass mix that you get for outdoor fireplaces," says Saghei.
With capacity to process up to 7,500 panels every day at the plant in Yuma, a surprisingly small amount goes to waste.
"Depending on the make and model of the panels... we're able to get up to 99 percent recovery rate."
- Logistics -
For Meng Tao, who specialises in sustainable energy infrastructure at Arizona State University, developing an efficient lifecycle for solar panels is a pressing issue.
With the United States among countries committed to weaning itself off fossil fuels following a landmark COP28 climate agreement, solar panel installation looks set to increase to a peak two decades from now.
"Once it matures, then the annual installation and the decommissioning will be about the same," he told AFP.
"But for the next 20 years... at least for the next 10 years... we'll just have more instalations than retirements."
The problem with recycling, he says, is not just that the value of recovered materials from panels can be relatively low, but also the logistics.
With panels distributed to thousands of sometimes far-flung rooftops, it can cost a lot of money just to get them to a recycling center.
And unlike some jurisdictions, the United States imposes the cost of removal and recycling on the end user -- making it more attractive for households just to dump their old units at the local landfill.
"There has to be some policy support" to plug the gap between what consumers will pay and the total lifecycle cost of the panels, says Tao.
- Growing market -
For Saghei, as for any business leaders, profitablity is important.
"You don't see too many getting into the business because recycling has a cost. It's not free. It's labor intensive. It's energy intensive," he says.
But he does see a way forward.
Recovering materials from old solar panels that can be put back into new solar panels is -- he is convinced -- a winning proposition.
"These are markets that are growing," he says.
"Right through this process we are able, once the industry scales to even larger figures, to put those raw commodities back into the supply chain.
"What's exciting is we're at the forefront."
A.Suleiman--SF-PST

