
-
 Freeski star Gu says injuries hit confidence as she targets Olympic treble
Freeski star Gu says injuries hit confidence as she targets Olympic treble
-
UK police search properties in Mandelson probe

-
 Bompastor extends contract as Chelsea Women's boss despite slump
Bompastor extends contract as Chelsea Women's boss despite slump
-
Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics open with glittering ceremony

-
 A French yoga teacher's 'hell' in a Venezuelan jail
A French yoga teacher's 'hell' in a Venezuelan jail
-
England's Underhill taking nothing for granted against Wales

-
 Fans cheer for absent Ronaldo as Saudi row deepens
Fans cheer for absent Ronaldo as Saudi row deepens
-
Violence-ridden Haiti in limbo as transitional council wraps up

-
 Hundreds protest in Milan ahead of Winter Olympics
Hundreds protest in Milan ahead of Winter Olympics
-
Suspect in murder of Colombian footballer Escobar killed in Mexico

-
 Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS Minnesota United
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS Minnesota United
-
Wainwright says England game still 'huge occasion' despite Welsh woes

-
 WADA shrugs off USA withholding dues
WADA shrugs off USA withholding dues
-
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron

-
 Winter Olympics to open with star-studded ceremony
Winter Olympics to open with star-studded ceremony
-
Trump posts, then deletes, racist clip of Obamas as monkeys

-
 Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe
-
Trump deletes racist video post of Obamas as monkeys

-
 Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS side Minnesota United
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS side Minnesota United
-
UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties

-
 Russian drone hits Ukrainian animal shelter
Russian drone hits Ukrainian animal shelter
-
US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests

-
 French cycling hope Seixas dreaming of Tour de France debut
French cycling hope Seixas dreaming of Tour de France debut
-
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source

-
 EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
-
Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque

-
 Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman
Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman
-
US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested

-
 Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
Arteta apologises to Rosenior after disrespect row

-
 Terror at Friday prayers: witness describes 'extremely powerful' blast in Islamabad
Terror at Friday prayers: witness describes 'extremely powerful' blast in Islamabad
-
Winter Olympics men's downhill: Three things to watch

-
 Ice dancers Chock and Bates shine as US lead Japan in team event
Ice dancers Chock and Bates shine as US lead Japan in team event
-
Stellantis takes massive hit on 'overestimation' of EV demand

-
 Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
-
Spanish PM urges caution as fresh rain heads for flood zone

-
 Iran says to hold more talks with US despite Trump military threats
Iran says to hold more talks with US despite Trump military threats
-
Russia accuses Kyiv of gun attack on army general in Moscow

-
 Cambodia reveals damage to UNESCO-listed temple after Thailand clashes
Cambodia reveals damage to UNESCO-listed temple after Thailand clashes
-
Norway crown princess 'deeply regrets' Epstein friendship

-
 Italy set for Winter Olympics opening ceremony as Vonn passes test
Italy set for Winter Olympics opening ceremony as Vonn passes test
-
England's Jacks says players back under-fire skipper Brook '100 percent'

-
 Carrick relishing Frank reunion as Man Utd host Spurs
Carrick relishing Frank reunion as Man Utd host Spurs
-
Farrell keeps the faith in Irish still being at rugby's top table

-
 Meloni, Vance hail 'shared values' amid pre-Olympic protests
Meloni, Vance hail 'shared values' amid pre-Olympic protests
-
Olympic freestyle champion Gremaud says passion for skiing carried her through dark times

-
 US urges new three-way nuclear deal with Russia and China
US urges new three-way nuclear deal with Russia and China
-
Indonesia landslide death toll rises to 74

-
 Hemetsberger a 'happy psychopath' after final downhill training
Hemetsberger a 'happy psychopath' after final downhill training
-
Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 31, wounds over 130


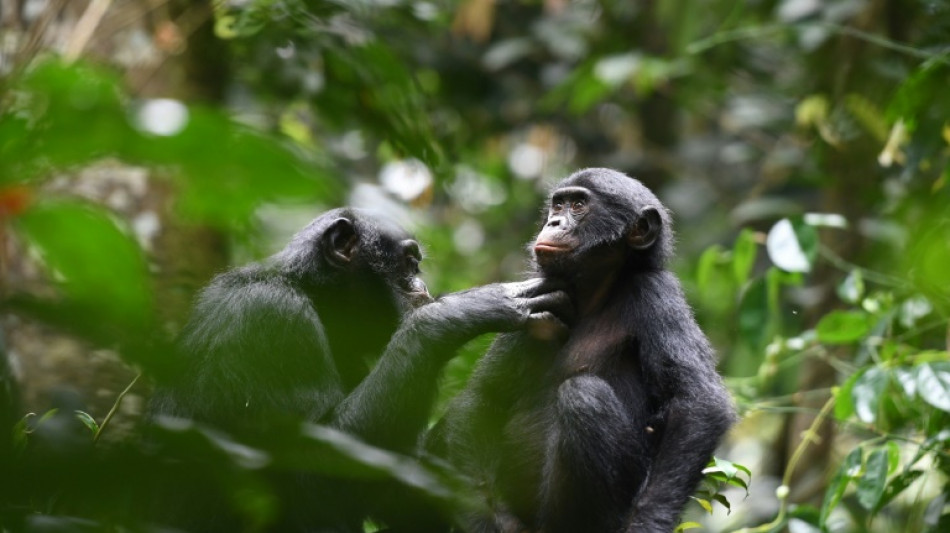
Good neighbors: Bonobo study offers clues into early human alliances
Human society is founded on our ability to cooperate with others beyond our immediate family and social groups.
And according to a study published Thursday in the journal Science, we're not alone: bonobos team up with outsiders too, in everything from grooming to food sharing, even forming alliances against sexual aggressors.
Lead author Liran Samuni of the German Primate Center in Gottingen told AFP that studying the primates offered a "window into our past," possibly signaling an evolutionary basis for how our own species began wider-scale collaborative endeavors.
Bonobos (Pan paniscus) are our closest living relatives, alongside chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes), and the two species are also very closely related to each other.
But while encounters between chimpanzee groups are inherently hostile and often result in lethal violence, interactions between bonobo parties hadn't been as well examined.
That's because bonobos, an endangered species, are notoriously difficult to study in their natural habitat -- and they live only in remote regions of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
With research on chimps dominating the literature, some scientists assumed hostility against outsiders was innate to human nature -- something we had perhaps trained ourselves to get past by inventing new social norms, even as that trait lurked deep inside.
- Female coalitions against sexual aggression -
In the new paper, Samuni teamed up with Martin Surbeck, a professor at Harvard who founded the Kokolopori Bonobo Reserve, to carry out a long-term study over two years.
"The first thing they do... is try to run away from you," Surbeck told AFP, explaining it took a long time for the bonobos to overcome their inherent fears of humans and behave normally.
Days began at 4:00 am and involved researchers trekking through the dark forest until they reached bonobo nests, then waiting for sunrise so they could follow the apes throughout the day, aided by indigenous Mongandu trackers.
Samuni and Surbeck focused on two small bonobo groups of 11 and 20 adults respectively, and found to their surprise they spent 20 percent of their total time together -- feeding, resting, traveling and more.
"Every individual is different," said Samuni. "There are those that are more introverts, extroverts, there are those that are more pro-social than others."
The team found that cooperation between the groups was driven largely by a select few who were more helpful within their own group. These individuals tended to connect with similar "pro-social" bonobos from the other group, creating a system of mutual benefit, or "reciprocal altruism."
The positive interactions occurred despite a low level of genetic relatedness between the groups, and despite the fact that reciprocity -- such as paying back a gift of fruit -- often took place much later, in future encounters.
Intriguingly, females, both within and from different groups, were found to form coalitions -- sometimes to chase an individual from a feeding tree, at other times to prevent a coercive sexual advance from a male.
"We don't see sexual coercion in bonobos, which is a common phenomenon in chimpanzees," said Surbeck. "One aspect of that might be due to those female coalitions, that help the females to maintain reproductive autonomy."
- Are we more like chimps or bonobos? -
The authors suggest their research offers an "alternative scenario" to the idea human cooperation is against our nature, or that we broadened cooperation with outsiders by first merging our extended families.
But "this does not mean that reconstructions of ancestral hominin species should be based only on bonobos," Joan Silk, a scientist at Arizona State University wrote in a related commentary.
There are other ways in which chimpanzees seem closer to humans than bonobos -- for example they more often hunt animal prey and use tools. Male chimpanzees also form strong bonds with fellow males and support them in aggressive acts, while bonobo males form stronger ties to females.
Understanding the natural selection forces that created these differences "may help to elucidate how and why humans became such an unusual ape," she concluded.
J.Saleh--SF-PST



