
-
 France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron
-
Winter Olympics to open with star-studded ceremony

-
 Trump posts, then deletes, racist clip of Obamas as monkeys
Trump posts, then deletes, racist clip of Obamas as monkeys
-
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe

-
 Trump deletes racist video post of Obamas as monkeys
Trump deletes racist video post of Obamas as monkeys
-
Colombia's Rodriguez signs with MLS side Minnesota United

-
 UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties
UK police probing Mandelson after Epstein revelations search properties
-
Russian drone hits Ukrainian animal shelter

-
 US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests
US says new nuclear deal should include China, accuses Beijing of secret tests
-
French cycling hope Seixas dreaming of Tour de France debut

-
 France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source
France detects Russia-linked Epstein smear attempt against Macron: govt source
-
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles

-
 Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque
Terror at Friday prayers: witnesses describe blast rocking Islamabad mosque
-
Iran expects more US talks after 'positive atmosphere' in Oman

-
 US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested
US says 'key participant' in 2012 attack on Benghazi mission arrested
-
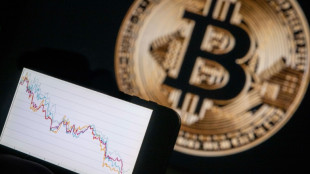
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
 Arteta apologises to Rosenior after disrespect row
Arteta apologises to Rosenior after disrespect row
-
Terror at Friday prayers: witness describes 'extremely powerful' blast in Islamabad

-
 Winter Olympics men's downhill: Three things to watch
Winter Olympics men's downhill: Three things to watch
-
Ice dancers Chock and Bates shine as US lead Japan in team event

-
 Stellantis takes massive hit on 'overestimation' of EV demand
Stellantis takes massive hit on 'overestimation' of EV demand
-
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer

-
 Spanish PM urges caution as fresh rain heads for flood zone
Spanish PM urges caution as fresh rain heads for flood zone
-
Iran says to hold more talks with US despite Trump military threats

-
 Russia accuses Kyiv of gun attack on army general in Moscow
Russia accuses Kyiv of gun attack on army general in Moscow
-
Cambodia reveals damage to UNESCO-listed temple after Thailand clashes

-
 Norway crown princess 'deeply regrets' Epstein friendship
Norway crown princess 'deeply regrets' Epstein friendship
-
Italy set for Winter Olympics opening ceremony as Vonn passes test

-
 England's Jacks says players back under-fire skipper Brook '100 percent'
England's Jacks says players back under-fire skipper Brook '100 percent'
-
Carrick relishing Frank reunion as Man Utd host Spurs

-
 Farrell keeps the faith in Irish still being at rugby's top table
Farrell keeps the faith in Irish still being at rugby's top table
-
Meloni, Vance hail 'shared values' amid pre-Olympic protests

-
 Olympic freestyle champion Gremaud says passion for skiing carried her through dark times
Olympic freestyle champion Gremaud says passion for skiing carried her through dark times
-
US urges new three-way nuclear deal with Russia and China

-
 Indonesia landslide death toll rises to 74
Indonesia landslide death toll rises to 74
-
Hemetsberger a 'happy psychopath' after final downhill training

-
 Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 31, wounds over 130
Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 31, wounds over 130
-
Elton John accuses UK tabloids publisher of 'abhorrent' privacy breaches

-
 Lindsey Vonn completes first downhill training run at Winter Olympics
Lindsey Vonn completes first downhill training run at Winter Olympics
-
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns

-
 Feyi-Waboso out of England's Six Nations opener against Wales
Feyi-Waboso out of England's Six Nations opener against Wales
-
Newcastle manager Howe pleads for Woltemade patience

-
 German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
-
Portugal heads for presidential vote, fretting over storms and far-right

-
 Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 30, wounds over 130: police
Suicide blast at Islamabad mosque kills at least 30, wounds over 130: police
-
Russia says Kyiv behind Moscow shooting of army general

-
 Greenland villagers focus on 'normal life' amid stress of US threat
Greenland villagers focus on 'normal life' amid stress of US threat
-
Iran, US hold talks in Oman after Trump military threats

-
 Stocks waver as tech worries build
Stocks waver as tech worries build
-
Dupont, Jalibert click to give France extra spark in Six Nations bid


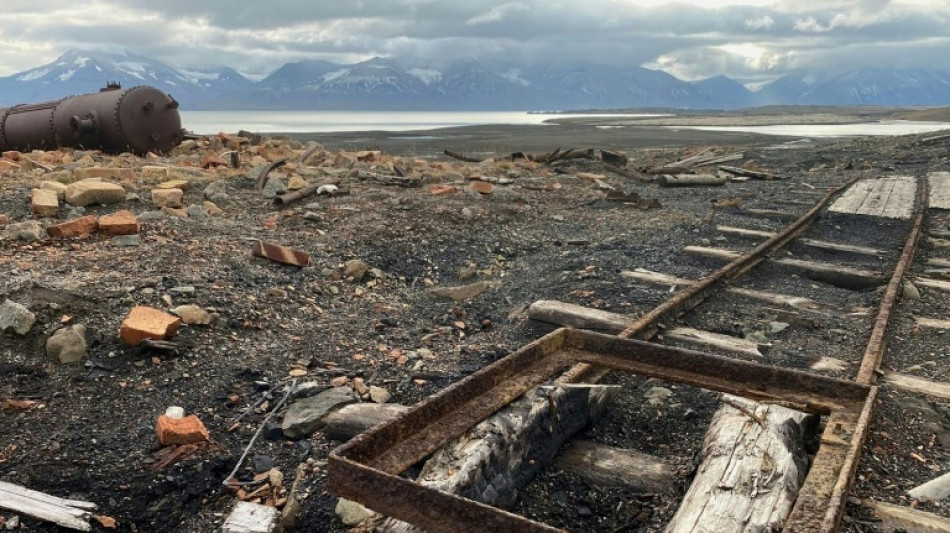
Arctic archipelago turns the page on its mining past
At the old Svea mine in the Arctic, broken railway tracks overgrown with weeds lead nowhere. Of the hundred buildings that once made up the town, there's almost nothing left.
Coal brought fortune to Norway's Svalbard archipelago, but that bonanza became a curse for the remote group of islands, now the most harmful fossil energy for the climate.
Svalbard, today home to 3,000 people and located in the fastest-warming region on the planet, is bit by bit erasing all traces of its mining past.
A 40-minute helicopter flight from the main town of Longyearbyen, the Svea mine and its surrounding settlement have been returned to Mother Nature after a massive, recently-completed restoration project.
"At its peak there were barracks for 300 people, with a canteen, an airfield with 35,000 passengers yearly, a power plant, a workshop, and storage," said Morten Hagen Johansen, in charge of the project at the mine where he was once employed.
The Svea site is the biggest natural restoration ever undertaken in Norway.
Only a handful of man-made objects remain, preserved because they are considered historic.
They include a few dilapidated brick buildings, a rusted track vehicle, and railway tracks that once transported wagons loaded with coal.
The area "was home to many miners who were working here for decades," Hanna Geiran, head of the Norwegian Directorate for Cultural Heritage, told AFP.
"Preserving these artefacts helps to better understand what this place was," she added.
- Avalanches -
The mine was opened by a Swedish company in 1917 and officially closed 100 years later after producing 34 million tonnes of coal.
The site has since been returned to its natural state at a cost of around 1.6 billion kroner (about $140 million) to the Norwegian state.
"The concept is to try to let nature take it back," said Hagen Johansen.
"That means to let creeks run freely. To make sure that avalanches do happen, because that will transport more sediment down and it will make new creeks."
The part of the Barents Sea where the Svalbard archipelago is located is warming up to seven times faster than the rest of the planet, according to a study published in last year.
At Svea, a spectacular landslide recently created a deep crevasse down a hilly slope.
"It is the result of a very heavy rainfall last summer where they got maybe 50-60 millimetres (2-2.3 inches) of rain in just 24 hours," geologist Fredrik Juell Theisen said.
"That was very unusual before climate change started changing the climate up here," he added.
- Russian presence -
The climate backlash is for the archipelago now trying to rid itself of fossil fuels.
Seven other mines located in the hills of Longyearbyen have almost all been closed, with the last one due to shut in 2025.
The town also disconnected its coal plant for good this month in exchange for a less-polluting diesel plant, ahead of a transition to renewable energies at a later stage.
Going forward, Svalbard's economy will rely on tourism and scientific research.
The only coal still being mined on the archipelago will be a vein in Barentsburg, a Russian mining community with just under 500 Russians and Ukrainians, most of them from the Donbas region.
Under the 1920 international treaty that recognises Norway's sovereignty over Svalbard, all signatories are entitled to exploit the region's natural resources equally.
As a result, Russia has for decades maintained a mining community om Svalbard, via the state-run company Trust Arktikugol, in a strategic region belonging to a NATO member.
According to some observers and Russia itself, strict environmental regulations that Norway has introduced in the region -- about two-thirds of Svalbard land is protected in one way or another -- are at least partly aimed at limiting .
It's impossible to know whether such considerations played into Oslo's decision to restore the Svea mine at great cost, said Mats Kirkebirkeland of Norwegian think tank Civita.
"But there's no denying that some of the Norwegian environmental policies and the geostrategic policies on Svalbard are aligned."
T.Khatib--SF-PST



