
-
 Voter swings raise midterm alarm bells for Trump's Republicans
Voter swings raise midterm alarm bells for Trump's Republicans
-
Australia dodges call for arrest of visiting Israel president

-
 Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
-
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life

-
 Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
-
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation

-
 New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
-
Family affair: Thailand waning dynasty still election kingmaker

-
 Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
-
Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment

-
 LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
-
Ukraine, Russia, US to start second day of war talks

-
 Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
-
Trump attacks US electoral system with call to 'nationalize' voting

-
 Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
-
US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy

-
 Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
-
Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football

-
 On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
-
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting

-
 AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
-
Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports

-
 Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
-
Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world

-
 Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
-
Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final

-
 Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
-
'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist

-
 BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report

-
 Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through

-
 No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
-
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
-
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery

-
 Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
-
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader

-
 Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
-
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum

-
 UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
-
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain

-
 Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
-
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act

-
 Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
-
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown

-
 Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
-
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends

-
 Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
-
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses

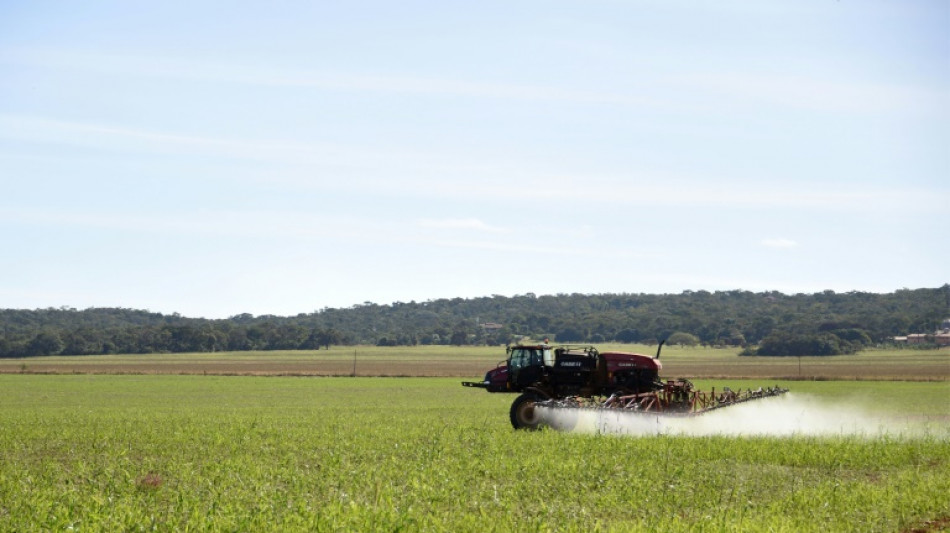
Emissions from fertilisers could be slashed by 2050: study
The production and use of nitrogen fertilisers accounts for five percent of global greenhouse gas emissions, which can be massively reduced with a few available interventions, a new study said Thursday.
Nitrogen fertilisers -- produced and used across the world -- are crucial for global food security.
But their harmful emissions contributing to global warming exceed the aviation sector, and are on par with the iron and steel, cement and plastics industries.
Most existing research has focused on emissions associated with the production of fertilisers, but Thursday's study showed that the majority -- two thirds -- come from the use of the fertilisers in croplands.
"There is the perception that the petrochemical industry has been causing the emissions producing the fertilisers, but actually that doesn't seem to be the case. That was very surprising for us," co-author Andre Cabrera Serrenho from Cambridge University told AFP.
The findings are important because they show "where we should prioritise action to reduce emissions," he added.
Carbon emissions could be reduced by up to 80 percent by 2050 while still producing enough food to feed a growing global population, said the study published Thursday in the journal Nature Food.
"The interventions we propose in our study do not imply loss in crop productivity, and they consider the future growing demand for food to feed a growing global population," Serrenho confirmed.
- Boost efficiency, use less -
Emissions associated with production are mostly associated with ammonia, a key ingredient in most fertilisers.
Making ammonia not only uses a lot of energy, but also requires hydrogen production, which causes emissions.
Some factories in China, for example, use coal to make hydrogen. Hydrogen can be made from water using electricity generated by renewables, which would greatly reduce emissions, though it is often a lot more expensive.
And since many factories producing ammonia for fertilisers, especially in Asia, are relatively new, they are less likely to covert technologies to be more environmentally friendly.
Switching to renewable energy in factories is another way to help reduce that carbon footprint.
But Serrenho said the main way to reduce emissions linked to fertilisers is on the use side, by increasing their efficiency and thus reducing their use.
"We are currently really inefficient in the way we use fertilisers," he said. "We put much more fertilisers in croplands than the amount of nitrogen that actually crops need to grow."
The main emissions in the use phase come from the degradation of fertiliser by bacteria that exist in the soil and produce nitrous oxide, one of the most powerful greenhouse gases.
Carbon dioxide and methane are also emitted in the use phase, but simply using less fertiliser could help to slash those harmful emissions.
But convincing farmers to use fertilisers more efficiently -- for example, applying them daily in smaller quantities instead of spraying in large doses them once a season -- will require policy shifts.
"If we could have more economic incentives to farmers to change practices to reduce emissions, that seems to be the most obvious place to start," Serrenho said.
R.Shaban--SF-PST



