
-
 Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
-
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life

-
 Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
-
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation

-
 New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
-
Family affair: Thailand waning dynasty still election kingmaker

-
 Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
-
Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment

-
 LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
-
Ukraine, Russia, US to start second day of war talks

-
 Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
-
Trump attacks US electoral system with call to 'nationalize' voting

-
 Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
-
US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy

-
 Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
-
Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football

-
 On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
-
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting

-
 AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
-
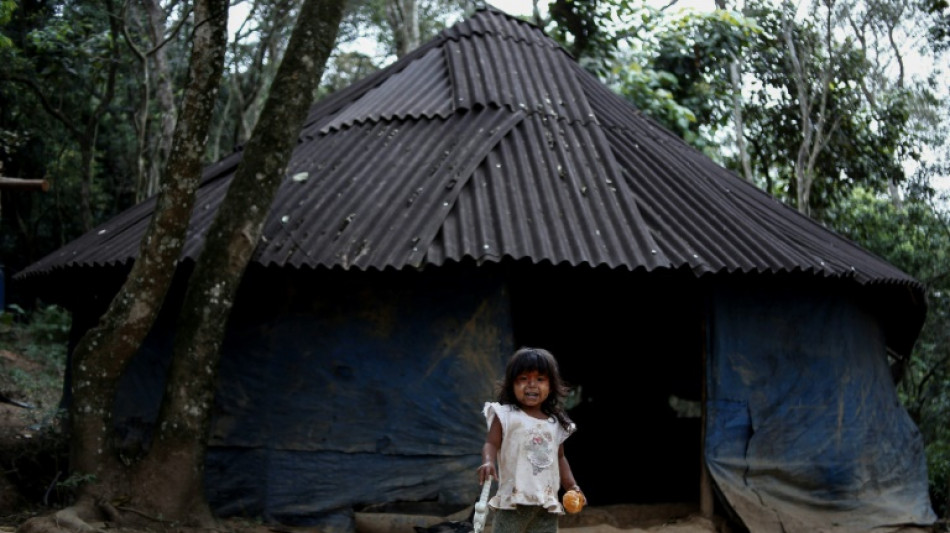
Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports

-
 Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
-
Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world

-
 Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
-
Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final

-
 Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
-
'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist

-
 BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report

-
 Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through

-
 No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
-
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
-
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery

-
 Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
-
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader

-
 Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
-
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum

-
 UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
-
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain

-
 Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
-
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act

-
 Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
-
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown

-
 Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
-
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends

-
 Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
-
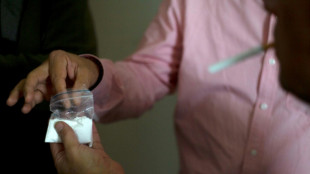
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
 Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study
-
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban


Indigenous land rights help protect Brazil's forests
Territories in Brazil's fragmented Atlantic Forest where Indigenous peoples enjoy secure land rights have seen measurably less deforestation than similar areas in which land tenure is weak or non-existent, researchers reported Thursday.
The findings, published in the journal PNAS Nexus, are the first to quantify the benefits of enhanced Indigenous land rights for Brazil's tropical rainforests, and add to a growing body of peer-reviewed literature highlighting more broadly the advantages of Indigenous stewardship.
"Even in highly developed and heavily deforested areas, granting land tenure to Indigenous peoples significantly improved forest outcomes," including less tree loss and more reforestation, lead author Rayna Benzeev, a researcher at the University of Colorado Boulder, told AFP.
"Each year after tenure was formalised, there was, on average, a 0.77 percent increase in forest cover compared to untenured lands," she added.
"That can add up over decades."
The Atlantic Forest -- Brazil's second-largest rainforest after the Amazon, stretching along 3,000 kilometres (1,860 miles) of coastline -- has been decimated by centuries of urbanisation, agriculture, logging and mining. It is home to 70 percent of the country's population, including Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro.
Only 12 percent of original forest area remains intact, versus about 80 percent for the Amazon.
Benzeev and colleagues looked at data on changes in forest cover and land tenure in 129 Atlantic Forest indigenous territories between 1985 and 2019.
They compared tree loss and reforestation within territories before and after land rights were granted, as well as across territories with different degrees of land tenure.
"Indigenous lands with tenure showed a reduction in deforestation and increase in reforestation compared to lands that didn't have secure legal rights," said Benzeev, writing from Brazil's Atlantic Forest, where she is sharing her findings with Indigenous leaders.
Jera Poty Mirim, a Guarani leader in the Tenonde Pora Indigenous Territory, said the study confirmed what Indigenous people already knew.
"Even before we reached the final step in obtaining recognition of strong rights to our lands, our people began to take care of our forests and to plant the traditional food crops of the Guarani," she told journalists this week.
- An ongoing challenge -
"But wherever communities have secure rights we can protect our forests better and invite partners to support our work to reforest the land destroyed by others."
On paper, Brazil provides robust legal protections for Indigenous rights. But in reality lax enforcement coupled with corruption has fuelled deforestation and illegal expropriation.
In the Atlantic Forest, encroachment by land grabbers, squatters and extractive industries -- whether mining or logging -- "remains an ongoing challenge for land defenders", the report's authors noted.
Those pressures surged during the administration of far-right President Jair Bolsonaro, who stepped down on January 1.
Incoming President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva has vowed to reverse those trends, and has set 2030 as a target for reaching zero deforestation.
"Titling the lands of Indigenous people is crucial if we want to guarantee the end of deforestation and preserve the global climate in balance," Paulo Moutinho, a senior scientist at Brazil's Amazon Environmental Research Institute (IPAM) and fellow at the Woodwell Climate Research Center, told AFP, commenting on the study.
The stakes for protecting the Amazon basin, the world's largest tropical biome, are both local and global.
Climate change coupled with forest destruction are pushing the Amazon basin toward a "tipping point" where it will shift from a tropical forest to a savannah-like state.
From 2000 to 2020, Brazil experienced a net loss of more than 20 million hectares of forest, or about six percent of total tree cover, according to Global Forest Watch.
B.Mahmoud--SF-PST


