
-
 Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
Countries using internet blackouts to boost censorship: Proton
-
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life

-
 Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
Thailand's pilot PM on course to keep top job
-
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation

-
 New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation
-
Family affair: Thailand waning dynasty still election kingmaker

-
 Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
Japan's first woman PM tipped for thumping election win
-
Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment

-
 LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
LA officials call for Olympic chief to resign over Epstein file emails
-
Ukraine, Russia, US to start second day of war talks

-
 Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club
-
Trump attacks US electoral system with call to 'nationalize' voting

-
 Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
-
US households become increasingly strained in diverging economy

-
 Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
Four dead men: the cold case that engulfed a Colombian cycling star
-
Super Bowl stars stake claims for Olympic flag football

-
 On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
On a roll, Brazilian cinema seizes its moment
-
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting

-
 AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
AI to track icebergs adrift at sea in boon for science
-
Indigenous Brazilians protest Amazon river dredging for grain exports

-
 Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
Google's annual revenue tops $400 bn for first time, AI investments rise
-
Last US-Russia nuclear treaty ends in 'grave moment' for world

-
 Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
Man City brush aside Newcastle to reach League Cup final
-
Guardiola wants permission for Guehi to play in League Cup final

-
 Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
Boxer Khelif reveals 'hormone treatments' before Paris Olympics
-
'Bad Boy,' 'Little Pablo' and Mordisco: the men on a US-Colombia hitlist

-
 BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
BHP damages trial over Brazil mine disaster to open in 2027
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA trade: report

-
 Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran-US talks back on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through

-
 No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf
-
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis
-
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery

-
 Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts
-
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader

-
 Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded
-
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum

-
 UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations
-
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain

-
 Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration
-
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act

-
 Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024
-
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown

-
 Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report
-
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends

-
 Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row
-
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
 Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study
-
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban


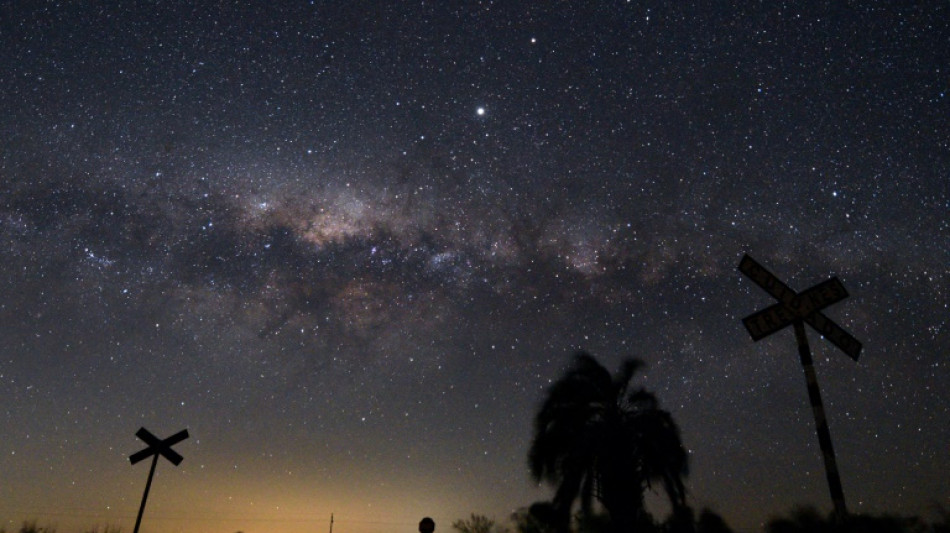
Star visibility eroding rapidly as night sky gets brighter: study
Light pollution is growing rapidly and in some places the number of stars visible to the naked eye in the night sky is being reduced by more than half in less than 20 years, according to a study released Thursday.
The researchers, whose findings were published in the journal Science, said the increase in light pollution -- skyglow -- that they found was much larger than that measured by satellite observations of Earth at night.
For the study of the change in global sky brightness from artificial light, the researchers used stellar observations from 2011 to 2022 submitted by more than 51,000 "citizen scientists" around the world.
Participants in the "Globe at Night" project run by the US National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory were given star maps and asked to compare them to the night sky at their location.
The change in the number of visible stars reported was equivalent to a 9.6 percent per year annual increase in sky brightness, averaged over the locations of the participants, the researchers said.
Over an 18-year period, given such star brightness change, a location with 250 visible stars would see that number reduced to 100.
Most of the naked-eye star observations came from Europe and the United States said Christopher Kyba, one of the authors of the study, but there was also good participation in Uruguay, South Africa and Japan.
"The global trend in skyglow that we measure likely underestimates the trend in countries with the most rapid increases in economic development, because the rate of change in light emission is highest there," the researchers said.
The study coincided with the replacement of many outdoor lights with light-emitting diodes (LEDs), but the researchers said the impact on skyglow from the transition to LEDs is unclear.
"Some researchers have predicted that it will be beneficial; others, that it could be harmful because of spectral changes or a rebound effect, in which the high luminous efficacy of LEDs leads to more or brighter lights being installed or longer hours of operation," they said.
According to the study, the global LED market share for new general lighting grew from under one percent in 2011 to 47 percent in 2019.
"The visibility of stars is deteriorating rapidly, despite (or perhaps because of) the introduction of LEDs in outdoor lighting applications," the researchers said.
"Existing lighting policies are not preventing increases in skyglow, at least on continental and global scales."
- 'Confronted with the cosmos' -
Kyba, a physicist at the German Research Center for Geoscience, told AFP that while the team was able to evaluate erosion of star visibility due to skyglow, not a lot of research has been done on its ecological impact.
"There's tons of research on light shining directly on animals and plants," he said. "But it's really hard to do experiments on the impact of skyglow.
"You're not going to do something like just turn off New York City and see what happens in the East River."
Science aside, light pollution has changed the character of the night sky.
"For all of human history, when people went outside at nighttime, they were sort of confronted with the cosmos, at least on clear nights with no moon," Kyba said.
"You'd walk outside and there's the stars, there's the Milky Way. It's there and it's shining down on you," he said.
"And now that's like a really unusual experience," he said. "It surely makes a difference to us as people that we don't have this experience that used to be a very universal experience."
The Globe at Night campaign hosts an interactive data map at globeatnight.org and is seeking volunteers to collect more observations in 2023.
R.Shaban--SF-PST


