
-
 Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
Lens cruise into French Cup quarters, Endrick sends Lyon through
-
No.1 Scheffler excited for Koepka return from LIV Golf

-
 Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
Curling quietly kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics
-
Undav pokes Stuttgart past Kiel into German Cup semis

-
 Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
Germany goalkeeper Ter Stegen to undergo surgery
-
Bezos-led Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
Iran says US talks are on, as Trump warns supreme leader
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 24 after Israel says officer wounded

-
 Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
Empress's crown dropped in Louvre heist to be fully restored: museum
-
UK PM says Mandelson 'lied' about Epstein relations

-
 Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
Shai to miss NBA All-Star Game with abdominal strain
-
Trump suggests 'softer touch' needed on immigration

-
 From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
From 'flop' to Super Bowl favorite: Sam Darnold's second act
-
Man sentenced to life in prison for plotting to kill Trump in 2024

-
 Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
Native Americans on high alert over Minneapolis crackdown
-
Dallas deals Davis to Wizards in blockbuster NBA deal: report

-
 Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
Russia 'no longer bound' by nuclear arms limits as treaty with US ends
-
Panama hits back after China warns of 'heavy price' in ports row

-
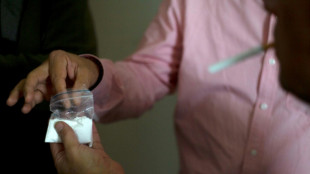 Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
Strike kills guerrillas as US, Colombia agree to target narco bosses
-
Wildfire smoke kills more than 24,000 Americans a year: study

-
 Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
Telegram founder slams Spain PM over under-16s social media ban
-
Curling kicks off sports programme at 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
Preventative cholera vaccination resumes as global supply swells: WHO
-
Wales' Macleod ready for 'physical battle' against England in Six Nations

-
 Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
Xi calls for 'mutual respect' with Trump, hails ties with Putin
-
'All-time great': Maye's ambitions go beyond record Super Bowl bid

-
 Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
Shadow over Vonn as Shiffrin, Odermatt headline Olympic skiing
-
US seeks minerals trade zone in rare Trump move with allies

-
 Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
Ukraine says Abu Dhabi talks with Russia 'substantive and productive'
-
Brazil mine disaster victims in London to 'demand what is owed'

-
 AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
AI-fuelled tech stock selloff rolls on
-
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' as nuclear pact ends with US

-
 White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
White says time at Toulon has made him a better Scotland player
-
Washington Post announces 'painful' job cuts

-
 All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
All lights are go for Jalibert, says France's Dupont
-
Artist rubs out Meloni church fresco after controversy

-
 Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
Palestinians in Egypt torn on return to a Gaza with 'no future'
-
US removing 700 immigration officers from Minnesota

-
 Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
Who is behind the killing of late ruler Gaddafi's son, and why now?
-
Coach Thioune tasked with saving battling Bremen

-
 Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
Russia vows to act 'responsibly' once nuclear pact with US ends
-
Son of Norway's crown princess admits excesses but denies rape

-
 US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
US calls for minerals trade zone in rare move with allies
-
Vowles dismisses Williams 2026 title hopes as 'not realistic'

-
 'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
'Dinosaur' Glenn chasing skating gold in first Olympics
-
Gaza health officials say strikes kill 23 after Israel says shots wounded officer

-
 Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
Italy foils Russian cyberattacks targeting Olympics
-
Stocks stabilise after Wall St AI-fuelled sell-off

-
 Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
Figure skating favourite Malinin feeling 'the pressure' in Milan
-
Netflix film probes conviction of UK baby killer nurse


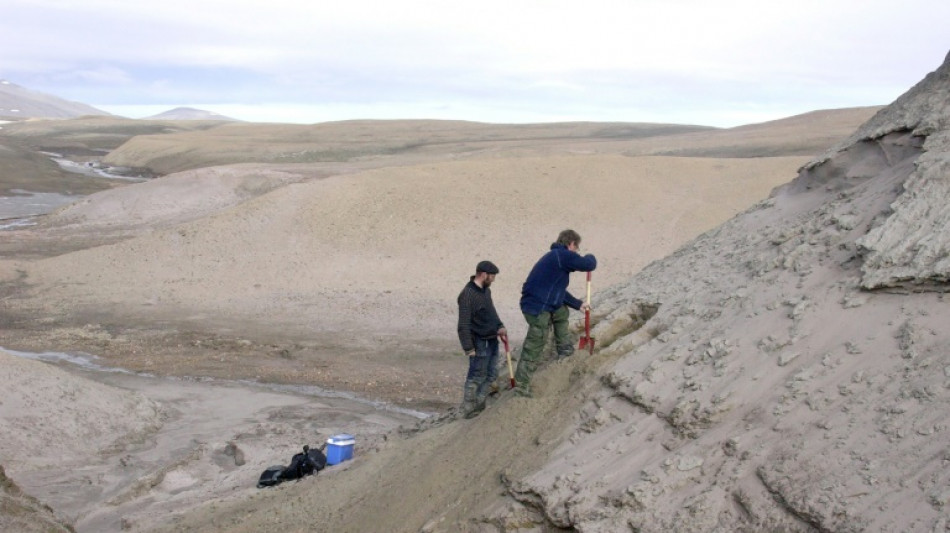
Scientists find 2-million year-old DNA in Greenland
Scientists in Greenland announced Wednesday they had found DNA dating back two million years -- the oldest ever extracted -- in sediment from the Ice Age, opening a new chapter in paleogenetics.
"We are breaking the barrier of what we thought we could reach in terms of genetic studies," said Mikkel Winther Pedersen, co-author of a new study published in science journal Nature.
"It was long thought that one million years was the boundary of DNA survival, but now we are twice as old" as that, told AFP.
They found the DNA fragments in sediment from the northernmost part of Greenland known as Kap Copenhagen, said the University of Copenhagen lecturer.
The fragments "come from an environment that we do not see anywhere on Earth today," he added. Frozen in a remote unpopulated area, the DNA had been very well preserved.
New technology enabled the scientists to determine that the 41 fragments were more than a million years older than the oldest known DNA, from a Siberian mammoth.
They had to first determine whether there was DNA hidden in the clay and quartz, then see whether it could be removed from the sediment to examine it.
The method used "provides a fundamental understanding of why minerals, or sediments, can preserve DNA", said Karina Sand, who heads the geobiology team at the University of Copenhagen and who took part in the study.
"It's a Pandora's box we're just about to open up", she added.
- Species adaptability -
The "rivers running through the environment transported minerals and organic material into the marine environment and this was where these terrestrial sediments were deposited", said Winther Pedersen.
Then, at some point around two million years ago, "this land mass beneath the water was raised up and became a part of North Greenland", he explained.
Today, Kap Copenhagen is an Arctic desert, where different types of deposits, including plant and insect fossils preserved in excellent condition, have already been discovered.
But scientists hadn't tried to establish the fossils' DNA, and very little was known about the presence of animals at the time.
The research team, which began its work in 2006, has now made it possible to paint a picture of what the region looked like two million years ago.
"We had this forested environment with mastodons and reindeer and hares running around in the landscape together with a lot of different plant species", he said, they had found 102 different kinds of plant.
The presence of mastodons was particularly noteworthy, he added, never having been found so far north before. The discovery has also given researchers more information about the adaptability of species.
Two million years ago, Greenland had temperatures 11 to 17 degrees warmer than today, but at its latitude, the sun doesn't set in summer nor rise in winter.
"We don't see this environment anywhere, this mix of species anywhere on Earth today", said Winther Pedersen.
"The plasticity in species, how species are actually able to adapt to different types of climate, might be different than what we previously thought.
"And obviously, it makes us look for newer and older sites.
"There are several different sites across the world that actually have geological deposits that go this far back. And even further back," ha added.
J.AbuHassan--SF-PST


