
-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
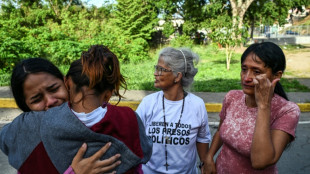
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket

-
 Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
-
Arsenal villain Martinelli turns FA Cup hat-trick hero

-
 Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
-
Kohli hits 93 as India edge New Zealand in ODI opener

-
 Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
-
Toulon win Munster thriller as Quins progress in Champions Cup

-
 NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Leeds rally to avoid FA Cup shock at Derby

-
 Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
-
Liverpool's Bradley out for the season with 'significant' knee injury

-
 Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
-
Comeback kid Hurkacz inspires Poland to first United Cup title

-
 Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
-
Salah and fellow stars aim to deny Morocco as AFCON reaches semi-final stage

-
 Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
-
Iran protest death toll rises as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
-
Venezuelans await release of more political prisoners, Maduro 'doing well'

-
 Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
-
Medvedev warms up in style for Australian Open with Brisbane win

-
 Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
-
Sabalenka fires Australian Open warning with Brisbane domination

-
 In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
-
New protests hit Iran as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
-
Keys draws on happy Adelaide memories before Australian Open defence

-
 Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
-
Ugandan opposition turns national flag into protest symbol

-
 Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
-
'Quad God' Malinin warms up for Olympics with US skating crown


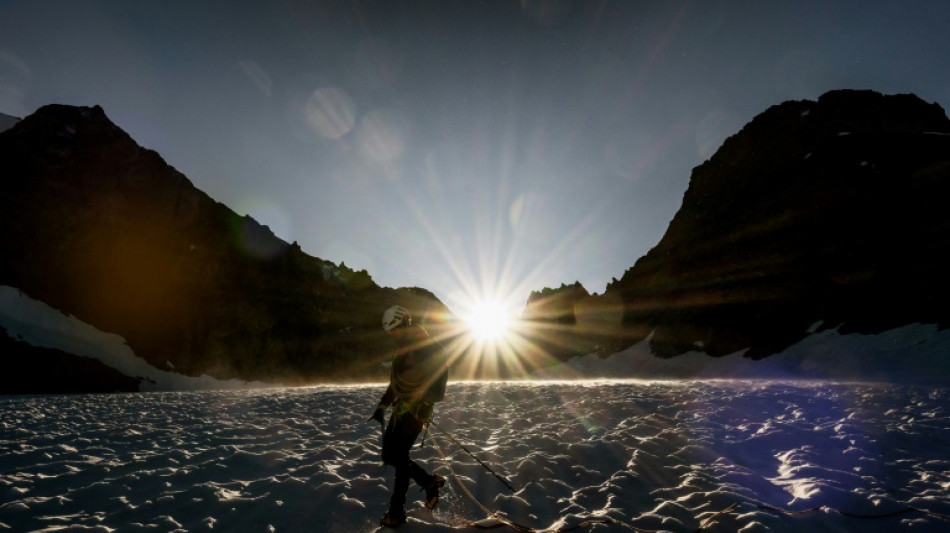
Heat melts Alps snow and glaciers, leaving water shortage
June's heatwave has caused French Alps snow and glaciers to melt faster, causing water shortages at mountain shelters just before the summer tourist hiking season gets into full swing.
"Everything has dried up," said Noemie Dagan, who looks after the Selle refuge, located at an altitude of 2,673 meters (8,769 feet) in the Ecrins, a mountain range overtowered by two majestic peaks.
The snowfield that usually supplies water to her 60-bed chalet already "looks a bit like what we would expect at the end of July or early August", she said.
"We are nearly a month early in terms of the snow's melting."
The mountain refuge, lacking a water tank, relies on water streaming down from the mountain. If it runs out it, the shelter will have to close.
This happened in mid-August 2023, and could happen again.
Dagan's backup solutions to avoid such a scenario include plastic pipes a kilometre long (0.6 mile) -- installed with difficulty -- to collect water from a nearby glacier close to the Pic de la Grave.
But the slopes along which the pipe was laid are steep, unstable and vulnerable to increasingly violent storms ravaging the range.
In the 15 years that she has worked in the sector, Dagan has witnessed "a metamorphosis" of the mountains and glaciers that are "our watertowers", she said.
"We are basically the sentinels who have seen what is coming."
- 'Never even crossed our minds' -
Thomas Boillot, a local mountain guide, said the possibility one day of seeing water supply issues affecting the mountain shelters had "never even crossed our minds".
But such cases have increased "and there will likely be more," he added.
Some snowfields once considered eternal now melt in the summer, precipitation has become scarcer, and glaciers change shape as they melt -- factors that combine to disrupt the water supply for chalets.
Water used to arrive "through gravity" from snow and ice reserves higher up, but it is going to have to be pumped from below in the future, he said.
Scientists say that the impact of climate change is nearly twice as severe in the Alps as it is globally, warning that only remnants of today's glaciers are likely to exist by 2100 -- if they haven't disappeared altogether by then.
This year's weather is also dangerous for the 1,400 glaciers in neighbouring Switzerland, where the authorities report that accumulated snow and ice have melted five to six weeks before the usual time.
"Brutal" is the term Xavier Cailhol, an environmental science PhD student and mountain guide, used to describe the impact of the heatwave that he saw on a recent trip to the massif of the Mont Blanc, western Europe's highest mountain.
"I started ski-touring on Mont Blanc in June with 40 centimetres (16 inches) of powder snow. I ended up on glaciers that were completely bare, even as high up as the Midi Peak, at 3,700 meters altitude," he said.
A cover of snow helps to protect the ice underneath by reflecting sunlight, he noted.
"Above 3,200 meters, it's drier than anything we've seen before," he said. "It's quite concerning for the rest of the summer."
A case in point is the accelerated melting of the Bossons Glacier, a massive ice tongue overlooking the valley before Chamonix.
It began with a "patch of gravel" which became larger, and "in fact is speeding up the melting at that location" because its dark colour absorbs more heat.
The melting of the Bossons Glacier is clearly visible from Chamonix, making it a constant reminder of what is happening to glaciers everywhere.
"It's a symbol," said Cailhol.
C.Hamad--SF-PST


