
-
 Chalamet, 'One Battle' among winners at Golden Globes
Chalamet, 'One Battle' among winners at Golden Globes
-
Turning point? Canada's tumultuous relationship with China

-
 Eagles stunned by depleted 49ers, Allen leads Bills fightback
Eagles stunned by depleted 49ers, Allen leads Bills fightback
-
Globes red carpet: chic black, naked dresses and a bit of politics

-
 Maduro's fall raises Venezuelans' hopes for economic bounty
Maduro's fall raises Venezuelans' hopes for economic bounty
-
Golden Globes kick off with 'One Battle' among favorites

-
 Australian Open 'underdog' Medvedev says he will be hard to beat
Australian Open 'underdog' Medvedev says he will be hard to beat
-
In-form Bencic back in top 10 for first time since having baby

-
 Swiatek insists 'everything is fine' after back-to-back defeats
Swiatek insists 'everything is fine' after back-to-back defeats
-
Wildfires spread to 15,000 hectares in Argentine Patagonia

-
 Napoli stay in touch with leaders Inter thanks to talisman McTominay
Napoli stay in touch with leaders Inter thanks to talisman McTominay
-
Meta urges Australia to change teen social media ban

-
 Venezuelans await political prisoners' release after government vow
Venezuelans await political prisoners' release after government vow
-
Lens continue winning streak, Endrick opens Lyon account in French Cup

-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
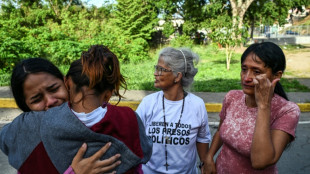
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket

-
 Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
-
Arsenal villain Martinelli turns FA Cup hat-trick hero

-
 Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
-
Kohli hits 93 as India edge New Zealand in ODI opener

-
 Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
-
Toulon win Munster thriller as Quins progress in Champions Cup

-
 NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Leeds rally to avoid FA Cup shock at Derby

-
 Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
-
Liverpool's Bradley out for the season with 'significant' knee injury

-
 Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
-
Comeback kid Hurkacz inspires Poland to first United Cup title

-
 Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
-
Salah and fellow stars aim to deny Morocco as AFCON reaches semi-final stage

-
 Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
-
Iran protest death toll rises as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'


Arctic warming spurs growth of carbon-soaking peatlands
Arctic peatlands are expanding as the climate warms, new research showed Thursday, a change that could slow global heating in the near term but have the opposite effect in future.
Peatlands are the largest terrestrial store of carbon, locking away twice as much heat-trapping CO2 from the atmosphere in their waterlogged soils as all the world's forests.
These carbon-rich reservoirs, composed of partially decayed organic matter, only cover three percent of Earth's surface, and generally fade out in the far north where harsh weather limits plant growth.
But warmer temperatures caused by climate change have improved growing conditions for plants in the Arctic, and satellite data has shown a general "greening" of this frosty region.
Using drones, satellite imagery and on-the-ground observations, an international team of scientists assessed peatlands in the European and Canadian Arctic to see if they had benefited from warmer climes.
They found strong evidence that peatlands "have likely undergone lateral expansion over the last 40 years" in the Arctic, which is the fastest warming region on Earth.
"The permafrost thaws a little, provides a water source for vegetation, and surface vegetation recovers. In this study, we specifically see a lateral expansion," Michelle Garneau, a professor at the University of Quebec in Montreal, and co-author of the study, told AFP.
The most marked change was observed where summer temperatures have risen the most, such as in the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard.
"All these new vegetated surfaces that didn't exist three decades ago are currently actively absorbing carbon," Garneau added.
This suggests Arctic peatlands "are an increasingly important natural carbon sink, at least in the near term", said study co-author Karen Anderson, a professor from the University of Exeter, which led the research.
But how they respond to climate change in future is "still highly uncertain", said the study published in the peer-reviewed journal Communications Earth and Environment.
Recent modelling suggests that northern peatlands "may become a carbon source from mid-century" as they dry out and permafrost thaws, the study said.
They are also at risk from wildfires, which release masses of stored up carbon at once.
"If temperatures continue to rise, we are likely to see changes in rainfall, and we are not sure how sustainable new or existing peatlands will be," said Anderson.
More peatlands also means more natural emissions of methane, a potent greenhouse gas far more effective at trapping heat than CO2.
"So while our study gives us some positive news, it does not detract from the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and stabilise our climate," said Anderson.
N.AbuHussein--SF-PST



