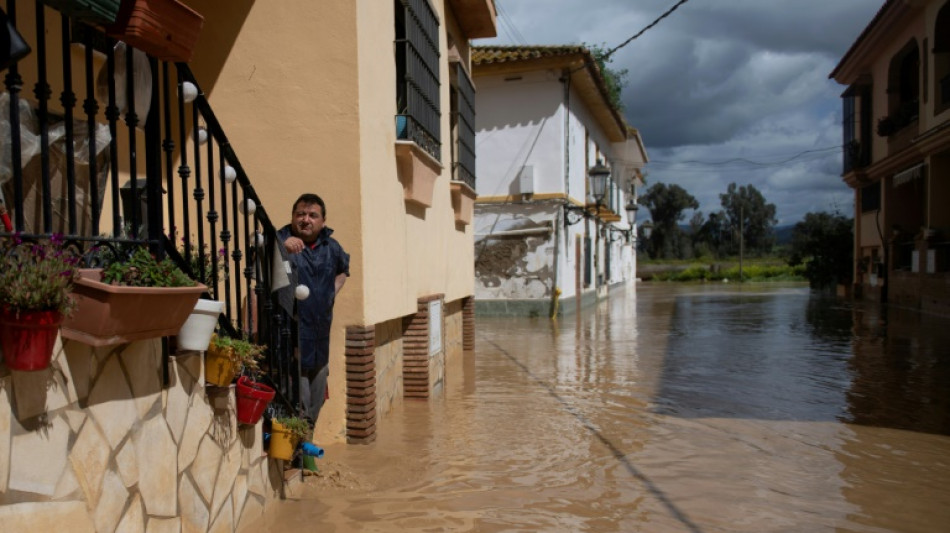

-
 Myanmar pro-military party claims Suu Kyi's seat in junta-run poll
Myanmar pro-military party claims Suu Kyi's seat in junta-run poll
-
Fed chair Powell says targeted by federal probe

-
 Trailblazing Milos Raonic retires from tennis
Trailblazing Milos Raonic retires from tennis
-
Australia recalls parliament early to pass hate speech, gun laws

-
 'One Battle After Another,' 'Hamnet' triumph at Golden Globes
'One Battle After Another,' 'Hamnet' triumph at Golden Globes
-
Japan aims to dig deep-sea rare earths to reduce China dependence

-
 Top UN court to hear Rohingya genocide case against Myanmar
Top UN court to hear Rohingya genocide case against Myanmar
-
US sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Trump says Iran 'want to negotiate' after reports of hundreds killed in protests
Trump says Iran 'want to negotiate' after reports of hundreds killed in protests
-
Bangladesh's powerful Islamists prepare for elections

-
 NBA-best Thunder beat the Heat as T-Wolves edge Spurs
NBA-best Thunder beat the Heat as T-Wolves edge Spurs
-
Ukraine's Kostyuk defends 'conscious choice' to speak out about war

-
 Trump says working well with Venezuela's new leaders, open to meeting
Trump says working well with Venezuela's new leaders, open to meeting
-
Asian equities edge up, dollar slides as US Fed Reserve subpoenaed

-
 Hong Kong court hears sentencing arguments for Jimmy Lai
Hong Kong court hears sentencing arguments for Jimmy Lai
-
Powell says Federal Reserve subpoenaed by US Justice Department

-
 Chalamet, 'One Battle' among winners at Golden Globes
Chalamet, 'One Battle' among winners at Golden Globes
-
Turning point? Canada's tumultuous relationship with China

-
 Eagles stunned by depleted 49ers, Allen leads Bills fightback
Eagles stunned by depleted 49ers, Allen leads Bills fightback
-
Globes red carpet: chic black, naked dresses and a bit of politics

-
 Maduro's fall raises Venezuelans' hopes for economic bounty
Maduro's fall raises Venezuelans' hopes for economic bounty
-
Golden Globes kick off with 'One Battle' among favorites

-
 Australian Open 'underdog' Medvedev says he will be hard to beat
Australian Open 'underdog' Medvedev says he will be hard to beat
-
In-form Bencic back in top 10 for first time since having baby

-
 Swiatek insists 'everything is fine' after back-to-back defeats
Swiatek insists 'everything is fine' after back-to-back defeats
-
Wildfires spread to 15,000 hectares in Argentine Patagonia

-
 Napoli stay in touch with leaders Inter thanks to talisman McTominay
Napoli stay in touch with leaders Inter thanks to talisman McTominay
-
Meta urges Australia to change teen social media ban

-
 Venezuelans await political prisoners' release after government vow
Venezuelans await political prisoners' release after government vow
-
Lens continue winning streak, Endrick opens Lyon account in French Cup

-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
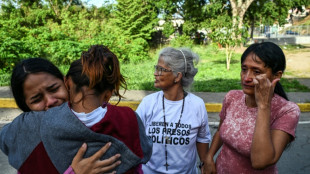
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket


World's 'exceptional' heat streak lengthens into March
Global temperatures hovered at historic highs in March, Europe's climate monitor said on Tuesday, prolonging an unprecedented heat streak that has pushed the bounds of scientific explanation.
In Europe, it was the hottest March ever recorded by a significant margin, said the Copernicus Climate Change Service, driving rainfall extremes across a continent warming faster than any other.
The world meanwhile saw the second-hottest March in the Copernicus dataset, sustaining a near-unbroken spell of record or near-record-breaking temperatures that has persisted since July 2023.
Since then, virtually every month has been at least 1.5 degrees Celsius hotter than it was before the industrial revolution, when humans began burning massive amounts of coal, oil and gas.
March was 1.6C above pre-industrial times, extending an anomaly so unusual that scientists are still trying to fully explain it.
"That we're still at 1.6C above preindustrial is indeed remarkable," said Friederike Otto of the Grantham Institute for Climate Change and the Environment at Imperial College London.
"We're very firmly in the grip of human-caused climate change," she told AFP.
Scientists had predicted the extreme run of global temperatures would subside after a warming El Nino event peaked in early 2024, but they have stubbornly lingered well into 2025.
"We are still experiencing extremely high temperatures worldwide. This is an exceptional situation," Robert Vautard, a leading scientist with the United Nations' climate expert panel IPCC, told AFP.
- 'Climate breakdown' -
Scientists warn that every fraction of a degree of global warming increases the intensity and frequency of extreme weather events such as heatwaves, heavy rainfall and droughts.
Climate change is not just about rising temperatures but the knock-on effect of all that extra heat being trapped in the atmosphere and seas by greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane.
Warmer seas mean higher evaporation and greater moisture in the atmosphere, causing heavier deluges and feeding energy into storms.
This also affects global rainfall patterns.
March in Europe was 0.26C above the previous hottest record for the month set in 2014, Copernicus said.
Some parts of the continent experienced the "driest March on record and others their wettest" for about half a century, said Samantha Burgess of the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, which runs the Copernicus climate monitor.
Bill McGuire, a climate scientist from University College London, said the contrasting extremes "shows clearly how a destabilised climate means more and bigger weather extremes".
"As climate breakdown progresses, more broken records are only to be expected," he told AFP.
Elsewhere in March, scientists said that climate change intensified a blistering heatwave across Central Asia and fuelled conditions for extreme rainfall which killed 16 people in Argentina.
- Puzzling heat -
The spectacular surge in global heat pushed 2023 and then 2024 to become the hottest years on record.
Last year was also the first full calendar year to exceed 1.5C -- the safer warming limit agreed by most nations under the Paris climate accord.
This single year breach does not represent a permanent crossing of the 1.5C threshold, which is measured over decades, but scientists have warned the goal is slipping out of reach.
According to Copernicus, global warming reached an estimated 1.36C above pre-industrial levels in October last year.
If the 30-year trend leading up to then continued, the world would hit 1.5C by June 2030.
Scientists are unanimous that burning fossil fuels has largely driven long-term global warming, and that natural climate variability can also influence temperatures from one year to the next.
But they are less certain about what else might have contributed to this record heat spike, or how this impacts our understanding about how climate might behave in future.
Vautard said there were "phenomena that remain to be explained" but the exceptional temperatures still fell within the upper range of scientific projections of climate change.
Experts think changes in global cloud patterns, airborne pollution and Earth's ability to store carbon in natural sinks like forests and oceans could be among factors contributing to the planet overheating.
Copernicus uses billions of measurements from satellites, ships, aircraft and weather stations to aid its climate calculations.
Its records go back to 1940 but other sources of climate data -- such as ice cores, tree rings and coral skeletons -- allow scientists to expand their conclusions using evidence from much further in the past.
Scientists say the current period is likely to be the warmest the Earth has been for the last 125,000 years.
C.Hamad--SF-PST



