
-
 'One Battle After Another,' 'Hamnet' triumph at Golden Globes
'One Battle After Another,' 'Hamnet' triumph at Golden Globes
-
Japan aims to dig deep-sea rare earths to reduce China dependence

-
 Top UN court to hear Rohingya genocide case against Myanmar
Top UN court to hear Rohingya genocide case against Myanmar
-
US sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Trump says Iran 'want to negotiate' after reports of hundreds killed in protests
Trump says Iran 'want to negotiate' after reports of hundreds killed in protests
-
Bangladesh's powerful Islamists prepare for elections

-
 NBA-best Thunder beat the Heat as T-Wolves edge Spurs
NBA-best Thunder beat the Heat as T-Wolves edge Spurs
-
Ukraine's Kostyuk defends 'conscious choice' to speak out about war

-
 Trump says working well with Venezuela's new leaders, open to meeting
Trump says working well with Venezuela's new leaders, open to meeting
-
Asian equities edge up, dollar slides as US Fed Reserve subpoenaed

-
 Hong Kong court hears sentencing arguments for Jimmy Lai
Hong Kong court hears sentencing arguments for Jimmy Lai
-
Powell says Federal Reserve subpoenaed by US Justice Department

-
 Chalamet, 'One Battle' among winners at Golden Globes
Chalamet, 'One Battle' among winners at Golden Globes
-
Turning point? Canada's tumultuous relationship with China

-
 Eagles stunned by depleted 49ers, Allen leads Bills fightback
Eagles stunned by depleted 49ers, Allen leads Bills fightback
-
Globes red carpet: chic black, naked dresses and a bit of politics

-
 Maduro's fall raises Venezuelans' hopes for economic bounty
Maduro's fall raises Venezuelans' hopes for economic bounty
-
Golden Globes kick off with 'One Battle' among favorites

-
 Australian Open 'underdog' Medvedev says he will be hard to beat
Australian Open 'underdog' Medvedev says he will be hard to beat
-
In-form Bencic back in top 10 for first time since having baby

-
 Swiatek insists 'everything is fine' after back-to-back defeats
Swiatek insists 'everything is fine' after back-to-back defeats
-
Wildfires spread to 15,000 hectares in Argentine Patagonia

-
 Napoli stay in touch with leaders Inter thanks to talisman McTominay
Napoli stay in touch with leaders Inter thanks to talisman McTominay
-
Meta urges Australia to change teen social media ban

-
 Venezuelans await political prisoners' release after government vow
Venezuelans await political prisoners' release after government vow
-
Lens continue winning streak, Endrick opens Lyon account in French Cup

-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
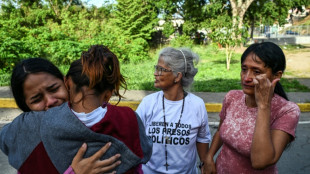
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket

-
 Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
-
Arsenal villain Martinelli turns FA Cup hat-trick hero

-
 Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
-
Kohli hits 93 as India edge New Zealand in ODI opener


Satellites link rain, drought intensity to global warming
The intensity of extreme water cycle events -- especially drought and precipitation or flooding -- correlates strongly with a continuing rise in global temperatures, according to a study published Monday.
Applying a novel method, researchers used satellite observations to quantify and rank more than a thousand extreme weather events over the last 20 years that have up to now defied easy measurement.
Rainfall and soil moisture -- or the lack of it -- have previously been the main yardstick for assessing intensity.
"Warm air increases evaporation so that more water is lost during droughts, and warm air also holds and transports more moisture, increasing precipitation during wet events," co-author Matthew Rodell of NASA told AFP.
"So what we are seeing –- greater intensity of extreme wet and dry events as the world warms -– makes sense."
Since 2015, the frequency of the highest category extreme events has increased to four per year, compared to three per year over the previous 13 years, the study reported.
The scientists were nonetheless surprised at how closely the pace of global warming tracked with the intensity of disruptions in the water cycle.
The impact was even stronger than naturally occurring El Nino and La Nina weather phenomena, they reported in the journal Nature Water.
The findings leave little doubt that increasing temperatures will cause more frequent, widespread and severe droughts and precipitation events in the future.
Earth's surface has warmed, on average, 1.2 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century, and -- on current policies -- is on track to heat up 2.8C above that benchmark by 2100.
By far the largest extreme event of the past 20 years was a sustained deluge over central Africa that "dwarfed" all the others measured.
- Bracing for worse -
It caused Lake Victoria to rise by over a metre (3.3 feet) and was still ongoing in 2021 when the study concluded.
"It's probable that the string of top-ten warmest years (2015-2023) is helping to sustain these ongoing events longer than they would have under more normal global temperature conditions," said Rodell.
About 70 percent of the events measured lasted six months or less, with an average duration of five to six months.
Roughly a third of the top 30 wet and dry events globally occurred in South America. More broadly, the correlations were particularly strong in tropical climates.
The most intense dry event registered happened in the Amazon during the hottest year on record.
The research offers concrete support for the IPCC's most recent assessment report, which found that the severity of extreme water cycle events is increasing.
Extreme droughts and floods are ranked as some of the world's worst disasters with huge impacts for the economy, agriculture and society.
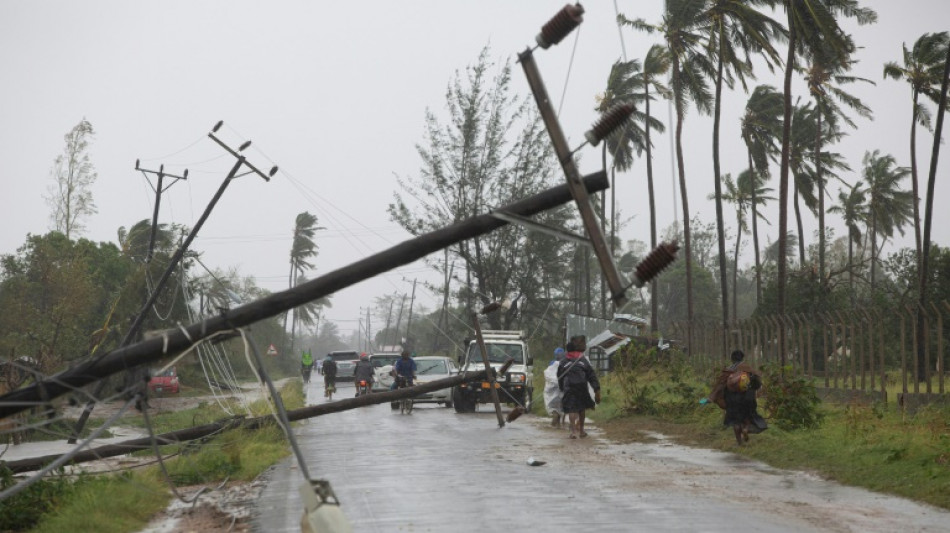
Tropical cyclone Freddy made a loop rarely seen by meteorologists when it returned to hit Mozambique for a second time on Monday, killing at least 70 people in Malawi and Mozambique and displacing thousands.
It is on track to be named the longest cyclone on record after its initial landfall in late February.
"The conclusion of this study suggests that preparation and adaptation will be that much more important in the future," said Rodell.
I.Yassin--SF-PST



