-
 US official says Venezuela freeing Americans in 'important step'
US official says Venezuela freeing Americans in 'important step'
-
2025 was third hottest year on record: EU, US experts

-
 Japan, South Korea leaders drum up viral moment with K-pop jam
Japan, South Korea leaders drum up viral moment with K-pop jam
-
LA28 organizers promise 'affordable' Olympics tickets

-
 K-pop heartthrobs BTS to kick off world tour in April
K-pop heartthrobs BTS to kick off world tour in April
-
Danish foreign minister heads to White House for high-stakes Greenland talks

-
 US allows Nvidia to send advanced AI chips to China with restrictions
US allows Nvidia to send advanced AI chips to China with restrictions
-
Sinner in way as Alcaraz targets career Grand Slam in Australia

-
 Rahm, Dechambeau, Smith snub PGA Tour offer to stay with LIV
Rahm, Dechambeau, Smith snub PGA Tour offer to stay with LIV
-
K-pop heartthrobs BTS to begin world tour from April

-
 Boeing annual orders top Airbus for first time since 2018
Boeing annual orders top Airbus for first time since 2018
-
US to take three-quarter stake in Armenia corridor

-
 Semenyo an instant hit as Man City close on League Cup final
Semenyo an instant hit as Man City close on League Cup final
-
Trump warns of 'very strong action' if Iran hangs protesters

-
 Marseille put nine past sixth-tier Bayeux in French Cup
Marseille put nine past sixth-tier Bayeux in French Cup
-
US stocks retreat from records as oil prices jump

-
 Dortmund outclass Bremen to tighten grip on second spot
Dortmund outclass Bremen to tighten grip on second spot
-
Shiffrin reasserts slalom domination ahead of Olympics with Flachau win

-
 Fear vies with sorrow at funeral for Venezuelan political prisoner
Fear vies with sorrow at funeral for Venezuelan political prisoner
-
Pittsburgh Steelers coach Tomlin resigns after 19 years: club

-
 Russell eager to face Scotland team-mates when Bath play Edinburgh
Russell eager to face Scotland team-mates when Bath play Edinburgh
-
Undav scores again as Stuttgart sink Frankfurt to go third

-
 Fuming French farmers camp out in Paris despite government pledges
Fuming French farmers camp out in Paris despite government pledges
-
Man Utd appoint Carrick as manager to end of the season

-
 Russia strikes power plant, kills four in Ukraine barrage
Russia strikes power plant, kills four in Ukraine barrage
-
France's Le Pen says had 'no sense' of any offence as appeal trial opens

-
 JPMorgan Chase reports mixed results as Dimon defends Fed chief
JPMorgan Chase reports mixed results as Dimon defends Fed chief
-
Vingegaard targets first Giro while thirsting for third Tour title

-
 US pushes forward trade enclave over Armenia
US pushes forward trade enclave over Armenia
-
Alpine release reserve driver Doohan ahead of F1 season

-
 Toulouse's Ntamack out of crunch Champions Cup match against Sale
Toulouse's Ntamack out of crunch Champions Cup match against Sale
-
US takes aim at Muslim Brotherhood in Arab world

-
 Gloucester sign Springbok World Cup-winner Kleyn
Gloucester sign Springbok World Cup-winner Kleyn
-
Trump tells Iranians 'help on its way' as crackdown toll soars

-
 Iran threatens death penalty for 'rioters' as concern grows for protester
Iran threatens death penalty for 'rioters' as concern grows for protester
-
US ends protection for Somalis amid escalating migrant crackdown

-
 Oil prices surge following Trump's Iran tariff threat
Oil prices surge following Trump's Iran tariff threat
-
Fashion student, bodybuilder, footballer: the victims of Iran's crackdown

-
 Trump tells Iranians to 'keep protesting', says 'help on its way'
Trump tells Iranians to 'keep protesting', says 'help on its way'
-
Italian Olympians 'insulted' by torch relay snub

-
 Davos braces for Trump's 'America First' onslaught
Davos braces for Trump's 'America First' onslaught
-
How AI 'deepfakes' became Elon Musk's latest scandal

-
 Albania's waste-choked rivers worsen deadly floods
Albania's waste-choked rivers worsen deadly floods
-
Cancelo rejoins Barca on loan from Al-Hilal

-
 India hunts rampaging elephant that killed 20 people
India hunts rampaging elephant that killed 20 people
-
Nuuk, Copenhagen mull Greenland independence in Trump's shadow

-
 WHO says sugary drinks, alcohol getting cheaper, should be taxed more
WHO says sugary drinks, alcohol getting cheaper, should be taxed more
-
Arteta urges Arsenal to learn from League Cup pain ahead of Chelsea semi

-
 Davos elite, devotees of multilateralism, brace for Trump
Davos elite, devotees of multilateralism, brace for Trump
-
Spanish star Julio Iglesias accused of sexual assault by two ex-employees


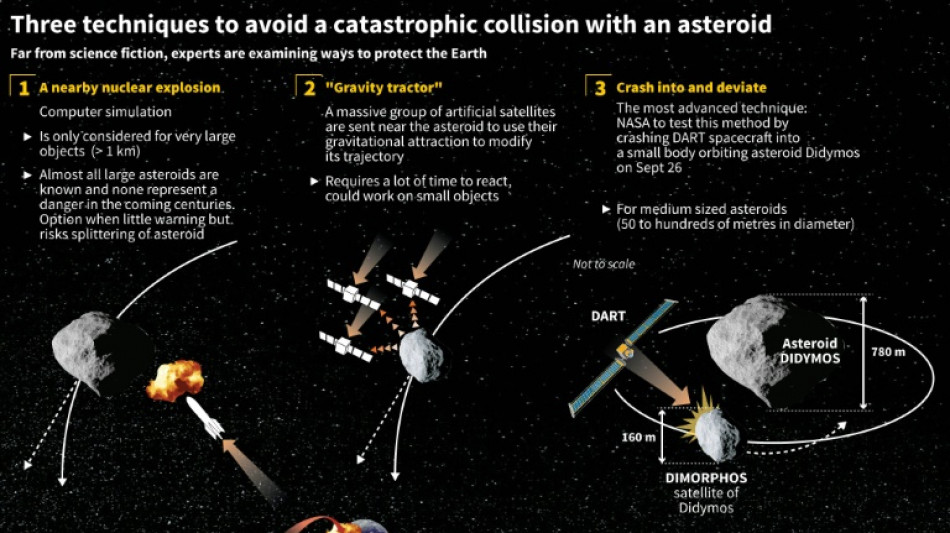
Direct impact or nuclear weapons? How to save Earth from an asteroid
NASA's DART mission to test deflecting an asteroid using "kinetic impact" with a spaceship is just one way to defend planet Earth from an approaching object -- and for now, the only method possible with current technology.
The operation is like playing billiards in space, using Newton's laws of motion to guide us.
If an asteroid threat to Earth were real, a mission might need to be launched a year or two in advance to take on a small asteroid, or decades ahead of projected impact for larger objects hundreds of kilometers in diameter that could prove catastrophic to the planet.
Or, a larger object might require hits with multiple spacecraft.
"This demonstration will start to add tools to our toolbox of methods that could be used in the future," said Lindley Johnson, NASA's planetary defense office, in a recent briefing.
Other proposed ideas have included a futuristic-sounding "gravity tractor," or a mission to blow up the hypothetical object with a nuclear weapon -- the method preferred by Hollywood.
- Gravity tractor -
Should an approaching object be detected early -- years or decades before it would hit Earth -- a spaceship could be sent to fly alongside it for long enough to divert its path via using the ship's gravitational pull, creating a so-called gravity tractor.
This method "has the virtue that the method of moving the asteroid is totally well understood -- it's gravity and we know how gravity works," Tom Statler, a DART program scientist at NASA said at a briefing last November when DART launched.
The mass of the spacecraft however would be a limiting factor -- and gravity tractors would be less effective for asteroids more than 500 meters in diameter, which are the very ones that pose the greatest threat.
In a 2017 paper, NASA engineers proposed a way to overcome this snag: by having the spacecraft scoop material from the asteroid to enhance its own mass, and thus, gravity.
But none of these concepts have been tried, and would need decades to build, launch and test.
- Nuclear detonation -
Another option: launching nuclear explosives to redirect or destroy an asteroid.
"This may be the only strategy that would be effective for the largest and most dangerous 'planet-killer' asteroids (more than one kilometer in diameter)," a NASA article on the subject says, adding such a strike might be useful as a "last resort" in case the other methods fail.
But these weapons are geopolitically controversial and technically banned from use in outer space.
Lori Glaze, NASA's planetary science division director said in a 2021 briefing that the agency believed the best way to deploy the weapons would be at a distance from an asteroid, in order to impart force on the object without blowing it into smaller pieces that could then multiply the threat to Earth.
A 2018 paper published in the "Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics" by Russian scientists looked at the direct detonation scenario.
E. Yu. Aristova and colleagues built miniature asteroid models and blasted them with lasers. Their experiments showed that blowing up a 200-meter asteroid would require a bomb 200 times as powerful as the one that exploded over Hiroshima in 1945.
They also said it would be most effective to drill into the asteroid, bury the bomb, then blow it up -- just like in the movie Armageddon.
H.Darwish--SF-PST



