
-
 Chalamet, 'One Battle' among winners at Golden Globes
Chalamet, 'One Battle' among winners at Golden Globes
-
Turning point? Canada's tumultuous relationship with China

-
 Eagles stunned by depleted 49ers, Allen leads Bills fightback
Eagles stunned by depleted 49ers, Allen leads Bills fightback
-
Globes red carpet: chic black, naked dresses and a bit of politics

-
 Maduro's fall raises Venezuelans' hopes for economic bounty
Maduro's fall raises Venezuelans' hopes for economic bounty
-
Golden Globes kick off with 'One Battle' among favorites

-
 Australian Open 'underdog' Medvedev says he will be hard to beat
Australian Open 'underdog' Medvedev says he will be hard to beat
-
In-form Bencic back in top 10 for first time since having baby

-
 Swiatek insists 'everything is fine' after back-to-back defeats
Swiatek insists 'everything is fine' after back-to-back defeats
-
Wildfires spread to 15,000 hectares in Argentine Patagonia

-
 Napoli stay in touch with leaders Inter thanks to talisman McTominay
Napoli stay in touch with leaders Inter thanks to talisman McTominay
-
Meta urges Australia to change teen social media ban

-
 Venezuelans await political prisoners' release after government vow
Venezuelans await political prisoners' release after government vow
-
Lens continue winning streak, Endrick opens Lyon account in French Cup

-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
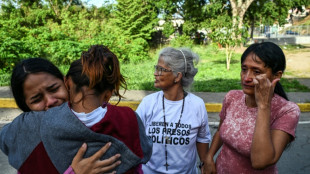
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket

-
 Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
-
Arsenal villain Martinelli turns FA Cup hat-trick hero

-
 Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
-
Kohli hits 93 as India edge New Zealand in ODI opener

-
 Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
-
Toulon win Munster thriller as Quins progress in Champions Cup

-
 NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Leeds rally to avoid FA Cup shock at Derby

-
 Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
-
Liverpool's Bradley out for the season with 'significant' knee injury

-
 Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
-
Comeback kid Hurkacz inspires Poland to first United Cup title

-
 Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
-
Salah and fellow stars aim to deny Morocco as AFCON reaches semi-final stage

-
 Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
-
Iran protest death toll rises as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'


Seeing Milky Way's new black hole is 'only the beginning': US researcher
At just 33 years old, Caltech assistant professor Katie Bouman is already a veteran of two major scientific discoveries.
The expert in computational imaging -- developing algorithms to observe distant phenomena -- helped create the program that led to the release of the first image of a black hole in a distant galaxy in 2019.
She quickly became something of a global science superstar, and was invited to testify before Congress about her work.
Now, she has again played a key role in the creation of a groundbreaking image of the supermassive black hole at the heart of our own Milky Way galaxy -- a cosmic body known as Sagittarius A*.
Her working group within the Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration, which revealed the stunning image Thursday, was tasked with piecing it together from the mass of data garnered by telescopes around the world.
Bouman spoke with AFP shortly after the breakthrough announcement.
- How does this discovery compare to 2019? -
"The first one was just so exciting because it was the first one, and just being able to see a black hole for the first time was spectacular. But I think the holy grail of the Event Horizon Telescope has always been to image Sagittarius A*.
"The reason why is because we have a lot more information from other observations on what we expected Sgr A* to look like. And so being able to see an image of that, it's much easier for us to see how it matches with what we expected from prior observations and theory.
"So I think that even though it is the second image that we're showing, it's actually a lot more exciting for that reason that we can actually use this to do more tests on our understanding of gravity."
- Why was it harder to see Sagittarius A*? -
"We collected the data for both M87* and Sgr A* in the same week in 2017, but it took us so much longer to make a picture of Sgr A* than M87*.
"Sgr A* has a lot of other things that are going on that make it a lot more challenging for us to make an image. We're actually observing the black hole through the plane of the galaxy. And that means that the gas in the galaxy actually scatters the image. It makes it look like we're looking at the black hole through, like, a frosted window, like in a shower. That's one challenge.
"But I would say the biggest challenge that we face is the fact that the black hole is evolving really quickly. The gas in M87* and Sgr A* is moving at roughly the same speed. But whereas it takes days to weeks to make a full orbit around M87*, for Sgr A*, it's evolving from minute to minute."
- Why are black holes so fascinating? -
"It just breaks with what we're used to here on Earth, right? Light can't even escape from it, and it's bending, it's warping space-time around it. It's just this mysterious thing and I think it just captures the imagination.
"What's cooler than working on black holes -- they're so mysterious, right? And the fact that we're able to make an image of one, something that should be unseeable... I think that that's just really exciting."
- What do you foresee in the future? A film? -
"I think this is really only the beginning. And now that we know that we have these extreme laboratories of gravity, we can go back and we can improve our instruments and improve our algorithms in order to see more and to extract more science.
"We made our first attempts at making a movie and we made a lot of progress, but we're not there yet -- where we feel we're confident enough that we feel, this is what Sgr A* looks like from minute to minute.
"So now we're going to go back, try to add more telescopes around the world, try to collect more data, so that we can actually show something that we feel really sure about."
Y.AlMasri--SF-PST




