
-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
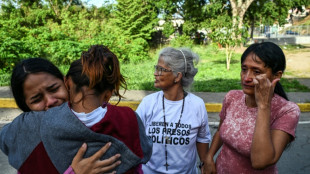
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket

-
 Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
-
Arsenal villain Martinelli turns FA Cup hat-trick hero

-
 Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
-
Kohli hits 93 as India edge New Zealand in ODI opener

-
 Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
-
Toulon win Munster thriller as Quins progress in Champions Cup

-
 NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Leeds rally to avoid FA Cup shock at Derby

-
 Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
-
Liverpool's Bradley out for the season with 'significant' knee injury

-
 Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
-
Comeback kid Hurkacz inspires Poland to first United Cup title

-
 Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
-
Salah and fellow stars aim to deny Morocco as AFCON reaches semi-final stage

-
 Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
-
Iran protest death toll rises as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
-
Venezuelans await release of more political prisoners, Maduro 'doing well'

-
 Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
-
Medvedev warms up in style for Australian Open with Brisbane win

-
 Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
-
Sabalenka fires Australian Open warning with Brisbane domination

-
 In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
-
New protests hit Iran as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
-
Keys draws on happy Adelaide memories before Australian Open defence

-
 Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
-
Ugandan opposition turns national flag into protest symbol

-
 Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
-
'Quad God' Malinin warms up for Olympics with US skating crown


Climate scorecard: good news and bad news
The task is clear -- stop burning fossil fuels, radically reduce energy demand and slash all planet-warming emissions in order to keep the planet cool enough so humans, animals and plants can survive and thrive.
So how do the actions of the world so far match up to the challenge?
Here is a rundown from the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's handbook on how to halt global warming:
- Emissions growth is slowing -
While we are continuing to spew more carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, the rate of that increase has slowed in recent years.
Emissions actually fell in 2020 -- by an estimated 5.8 percent compared to 2019 -- as governments around the world imposed unprecedented lockdowns to try to halt the spread of Covid-19.
Demand for energy shrank in almost all areas -- except residential buildings. International aviation emissions were down some 45 percent.
Meanwhile, at least 24 countries in the world have managed to cut greenhouse gas emissions and consumption-based CO2 pollution for a decade or more. Almost all are in Europe, although the list also includes the United States and Jamaica.
- But they need to fall, and fast -
Emissions have already rebounded from the pandemic.
Developing nations that have come from a low base per capita are seeing sharp increases.
And carbon footprints per person in rich countries remain stubbornly high, particularly in Australia, Canada.
- We have most of the means -
There are a range of low-carbon technologies to produce electricity and these are becoming cheaper, better and more widely used. These include solar photovoltaics (PV), onshore and offshore wind, and batteries.
"In many contexts solar PV and onshore wind power are now competitive with fossil-based generation," the report said.
Since 2010 emissions from coal have grown, but more slowly, as the US and Europe retired some old plants, while China added fewer new ones. A large number of planned coal plants around the world were either scrapped or converted so that they could also burn biomass.
- But we struggle to kick the dirty fuel habit -
All of the world's electricity will have to come from low-carbon generation by 2050 to meet the Paris Agreement global warming targets. This is "challenged" by growing electricity demand.
Currently, solar PV and wind generation technologies account for less than 10 percent of the market.
Despite coal's hefty C02 emissions, some countries and even international development banks continue to fund and develop new coal capacity.
- We can transform transport, buildings and industry -
Electrification is a "feasible, scalable and affordable" option to decarbonise mass transportation.
Electric vehicles (EVs) are the fastest-growing part of the automobile industry and if these cars and trucks are charged with low-carbon electricity they can significantly reduce emissions.
It is possible to make existing and new buildings in all parts of the world either nearly zero-energy or low-energy.
Most industrial processes in general can be decarbonised through a combination of technology using electricity and hydrogen, carbon capture and innovation in the circular use of materials (i.e. recycling and reusing).
- But change is slow -
Transport emissions grew at an average of two percent a year per between 2010 and 2019, due to continued "high travel demand, heavier vehicles, low efficiencies and car-centric development".
Beyond charging EVs with zero-emissions electricity, car manufacturing, shipping and aviation also need to be decarbonised, as do supply chains in general.
As for construction, the low ambition of government policies is a particular concern, for both existing buildings in developed countries and new buildings in developing ones.
The strong global demand for basic materials means industrial emissions continue to grow. This demand must be sharply reduced, alongside the rapid scale up of low-carbon innovations, otherwise there is a risk of locking in emissions "for decades to come".
- A crescendo of climate action -
An increasing number of countries say they plan to achieve "net-zero" C02, or greenhouse gas, emissions by mid-century.
Mandatory policies like pricing and regulation have expanded, while many businesses have promised to curb emissions.
Climate activism is growing, labour unions are starting to engage with the issues, while media coverage of climate change is increasing and becoming better at accurately reflecting the science.
- But action needs to happen faster -
Current national pledges under the Paris Agreement will not limit global warming to the target of 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Many net-zero targets are "ambiguously defined" and the policies to achieve them are not yet in place.
Low-carbon alternatives need much more investment, while "status quo interests" are acting to block progress.
People are also subjected to misinformation on online and in traditional media that has "undermined significantly" understanding of the science.
R.Halabi--SF-PST




