
-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
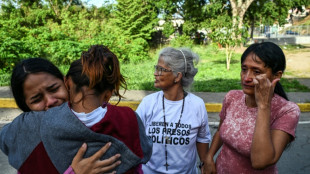
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket

-
 Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
-
Arsenal villain Martinelli turns FA Cup hat-trick hero

-
 Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
-
Kohli hits 93 as India edge New Zealand in ODI opener

-
 Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
-
Toulon win Munster thriller as Quins progress in Champions Cup

-
 NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Leeds rally to avoid FA Cup shock at Derby

-
 Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
-
Liverpool's Bradley out for the season with 'significant' knee injury

-
 Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
-
Comeback kid Hurkacz inspires Poland to first United Cup title

-
 Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
-
Salah and fellow stars aim to deny Morocco as AFCON reaches semi-final stage

-
 Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
-
Iran protest death toll rises as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
-
Venezuelans await release of more political prisoners, Maduro 'doing well'

-
 Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
-
Medvedev warms up in style for Australian Open with Brisbane win

-
 Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
-
Sabalenka fires Australian Open warning with Brisbane domination

-
 In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
-
New protests hit Iran as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
-
Keys draws on happy Adelaide memories before Australian Open defence

-
 Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
-
Ugandan opposition turns national flag into protest symbol

-
 Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
-
'Quad God' Malinin warms up for Olympics with US skating crown


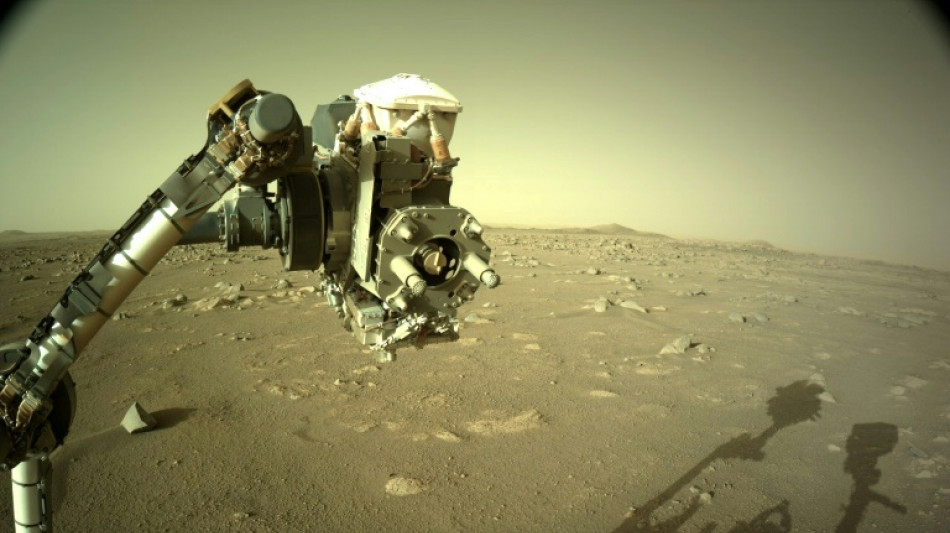
First audio recorded on Mars reveals two speeds of sound
The first audio recordings on Mars reveal a quiet planet with occasional gusts of wind where two different speeds of sound would have a strange delayed effect on hearing, scientists said Friday.
After NASA's Perseverance rover landed on Mars in February last year, its two microphones started recording, allowing scientists to hear what it is like on the Red Planet for the first time.
In a study published in the Nature journal on Friday, the scientists gave their first analysis of the five hours of sound picked up by Perseverance's microphones.
The audio revealed previously unknown turbulence on Mars, said Sylvestre Maurice, the study's main author and scientific co-director of the shoebox-sized SuperCam mounted on the rover's mast which has the main microphone.
The international team listened to flights by the tiny Ingenuity helicopter, a sister craft to Perseverance, and heard the rover's laser zap rocks to study their chemical composition -- which made a "clack clack" sound, Maurice told AFP.
"We had a very localised sound source, between two and five metres (six to 16 metres) from its target, and we knew exactly when it was going to fire," he said.
The study confirmed for the first time that the speed of sound is slower on Mars, travelling at 240 metres per second, compared to Earth's 340 metres per second.
This had been expected because Mars' atmosphere is 95 percent carbon dioxide -- compared to Earth's 0.04 percent -- and is about 100 times thinner, making sound 20 decibels weaker, the study said.
- 'I panicked' -
But the scientists were surprised when the sound made by the laser took 250 metres a second -- 10 metres faster than expected.
"I panicked a little," Maurice said. "I told myself that one of the two measurements was wrong because on Earth you only have one speed of sound."
They had discovered there are two speeds of sound on the surface of Mars -- one for high-pitched sounds like the zap of the laser, and another for lower frequencies like the whir of the helicopter rotor.
This means that human ears would hear high-pitched sounds slightly earlier.
"On Earth, the sounds from an orchestra reach you at the same speed, whether they are low or high. But imagine on Mars, if you are a little far from the stage, there will be a big delay," Maurice said.
"All of these factors would make it difficult for two people to have a conversation only five metres (16 feet) apart", the French CNRS research institute said in a statement.
- 'Scientific gamble' pays off -
It was otherwise so quiet on Mars that the scientists repeatedly feared something was wrong, the CNRS said, possibly provoking memories of two failed previous attempts in 1999 and 2008 to record sound there.
"There are few natural sound sources with the exception of the wind," the scientists said in a statement linked to the study.
The microphones did pick up numerous "screech" and "clank" sounds as the rover's metal wheels interacted with rocks, the study said.
The recording could also warn about problems with the rover -- like how drivers sense something's wrong when their car starts making strange noises.
Maurice said he felt the "scientific gamble" of taking microphones to Mars was a success.
Thierry Fouchet of the Paris Observatory, who was also involved in the research, said that listening to turbulence, such as vertical winds known as convection plumes, will "allow us to refine our numerical models for predicting climate and weather".
Future missions to Venus or Saturn's moon Titan could also now come equipped with microphones.
And Perseverance is far from done eavesdropping. While its core mission lasts just over two years, it could remain operational well beyond that -- the Curiosity rover is still kicking nine years into a planned two-year stint.
Q.Najjar--SF-PST




