
-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
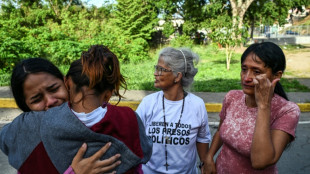
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket

-
 Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
-
Arsenal villain Martinelli turns FA Cup hat-trick hero

-
 Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
-
Kohli hits 93 as India edge New Zealand in ODI opener

-
 Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
-
Toulon win Munster thriller as Quins progress in Champions Cup

-
 NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Leeds rally to avoid FA Cup shock at Derby

-
 Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
-
Liverpool's Bradley out for the season with 'significant' knee injury

-
 Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
-
Comeback kid Hurkacz inspires Poland to first United Cup title

-
 Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
-
Salah and fellow stars aim to deny Morocco as AFCON reaches semi-final stage

-
 Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
-
Iran protest death toll rises as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
-
Venezuelans await release of more political prisoners, Maduro 'doing well'

-
 Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
-
Medvedev warms up in style for Australian Open with Brisbane win

-
 Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
-
Sabalenka fires Australian Open warning with Brisbane domination

-
 In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
-
New protests hit Iran as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
-
Keys draws on happy Adelaide memories before Australian Open defence

-
 Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
-
Ugandan opposition turns national flag into protest symbol

-
 Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
-
'Quad God' Malinin warms up for Olympics with US skating crown


Nations vet 3,000-page handbook to halt climate crisis
Nearly 200 nations gather Monday to grapple with a question that will outlive Covid-19 and Russia's invasion of Ukraine: how does a world addicted to fossil fuels prevent carbon pollution from making Earth unliveable?
A partial answer is set for April 4 after closed-door, virtual negotiations approve a nearly 3,000-page report detailing options for drawing down greenhouse gases and extracting them from the air.
"The impacts are costly and mounting, but we still have some time to close the window and get ahead of the worst of them if we act now," said Alden Meyer, a senior analyst at climate and energy think-tank E3G.
"This report will supply the answers as to what we need if we're serious about getting there."
In August 2021, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) laid out the physical science: the pace of global warming and sea level rise, along with shifts in the frequency, duration and intensity of cyclones, heatwaves and droughts.
That was part one in a three-part assessment, the sixth since 1990.
It projected that Earth's surface temperature will rise 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels, perhaps within a decade.
A 1.5C cap on global warming -- the aspirational goal of the 2015 Paris climate accord -- has been embraced as a target by most of the world's nations.
It's not hard to see why: barely 1.1C of warming so far has ushered in a crescendo of deadly extreme weather across the globe.
Recently renewed national carbon-cutting commitments, however, still put us on a catastrophic path toward 2.7C of warming by 2100.
- 'Overshooting' 1.5C -
Part two of the IPCC report -- described by UN chief Antonio Guterres as an "atlas of human suffering" -- details past and future climate impacts and the limits of our ability to adapt.
Delaying climate action would severely reduce the chances of a "livable future," it concluded.
Part three is about how to keep planet-warming gases out of the atmosphere, with chapters on the key sectors where rapid and deep change is needed: energy, transport, industry, agriculture, among others.
"We are talking about the large-scale transformation of all the major systems," climate economist and co-author Celine Guivarch told AFP.
The main focus is on weaning the global economy of fossil fuels and moving to low- or zero-carbon sources of energy, from solar and wind to nuclear, hydro and hydrogen.
Helping that transition is the fact that renewable energy is now cheaper than energy generated by fossil fuels in many markets.
The IPCC also details ways to reduce demand for oil, gas and coal, whether by making buildings more energy efficient or encouraging shifts in lifestyle, such as eating less beef and not flying half-way around the world for a week-long holiday.
But humanity has waited so long to take action that switching supply and reducing demand are not enough: we also need to pull CO2 out of the air.
In theory -- because the technology does not yet exist at scale -- carbon dioxide removal will compensate for hard-to-decarbonise sectors such as aviation and shipping, and extract excess CO2 if temperatures "overshoot" the Paris Agreement targets.
- Likely to fail? -
"Delivering on the climate commitments that we've made internationally and nationally is far more challenging than we have been prepared to accept," said Kevin Anderson, a professor of energy and climate change at the University of Manchester.
"Right now, we are very likely to fail. But if we don't try, we are guaranteed to fail," he told AFP.
The IPCC "solutions" report draws from hundreds of models projecting development pathways that keep Earth within the bounds of the Paris temperature goals.
"There are scenarios that show high renewables and low nuclear, and scenarios that show the opposite," said Taryn Fransen, an analyst at the World Resources Institute in Washington DC.
"This report lays out those pathways. Now it's up now to our leaders to take that to heart."
Besides feeding into UN political negotiations, which resume in November in Egypt at COP 27, the IPCC findings will also be important "for the conversation going on in the US and Europe around the need to transition away from Russian oil and gas," said Meyer.
The head of the IPCC delegation from Ukraine made this point in a dramatic statement at a closed plenary in February, only days after Russian troops invaded her country.
"Human-induced climate change and the war on Ukraine have the same roots -- fossil fuels -- and our dependence on them," said Svitlana Krakovska, according to multiple sources.
V.Said--SF-PST




