
-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket

-
 Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
-
Arsenal villain Martinelli turns FA Cup hat-trick hero

-
 Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
-
Kohli hits 93 as India edge New Zealand in ODI opener

-
 Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
-
Toulon win Munster thriller as Quins progress in Champions Cup

-
 NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Leeds rally to avoid FA Cup shock at Derby

-
 Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
-
Liverpool's Bradley out for the season with 'significant' knee injury

-
 Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
-
Comeback kid Hurkacz inspires Poland to first United Cup title

-
 Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
-
Salah and fellow stars aim to deny Morocco as AFCON reaches semi-final stage

-
 Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
-
Iran protest death toll rises as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
-
Venezuelans await release of more political prisoners, Maduro 'doing well'

-
 Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
-
Medvedev warms up in style for Australian Open with Brisbane win

-
 Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
-
Sabalenka fires Australian Open warning with Brisbane domination

-
 In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
-
New protests hit Iran as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
-
Keys draws on happy Adelaide memories before Australian Open defence

-
 Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
-
Ugandan opposition turns national flag into protest symbol

-
 Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
-
'Quad God' Malinin warms up for Olympics with US skating crown


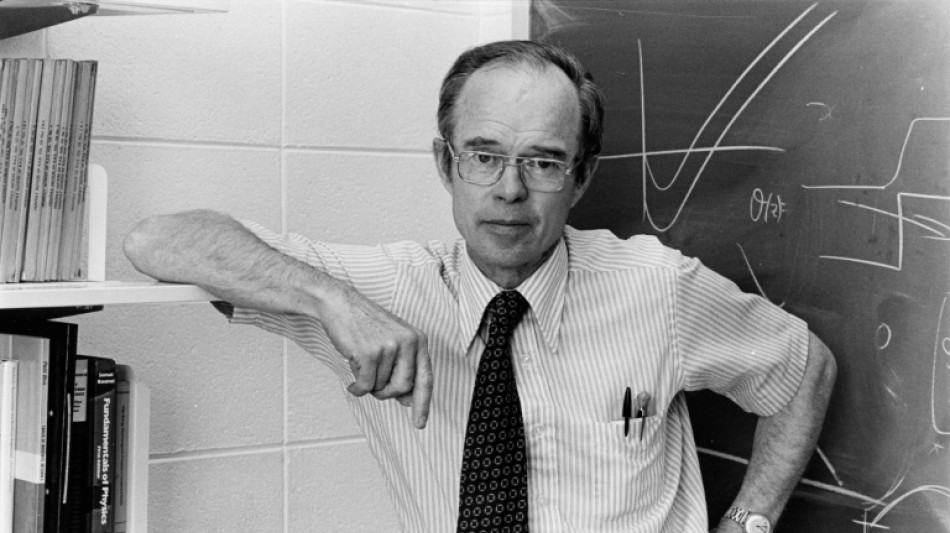
'Visionary' US astrophysicist Eugene Parker dead at 94
Eugene Parker, a pioneering American astrophysicist whose mathematical prediction that charged particles streamed from stars in a solar wind was met with disbelief before he was ultimately vindicated, has died aged 94, NASA said on Wednesday.
Parker was hailed as a visionary who laid the groundwork for the field of heliophysics, the science of understanding the Sun and its interactions with Earth and the solar system, including space weather.
In 2018, he became the first person to witness the launch of a spacecraft bearing his name, NASA's Parker Solar Probe.
"We were saddened to learn the news that one of the great scientific minds and leaders of our time has passed," said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson in a statement. Parker died Tuesday, according to the University of Chicago, his longtime academic home.
"Gene Parker was a legendary figure in our field -- his vision of the Sun and the solar system was way ahead of his time," added Angela Olinto, dean of the Physical Sciences Division at the University of Chicago.
Born on June 10, 1927 in Michigan, Parker earned a bachelor's degree in physics from Michigan State University and a PhD from Caltech, then taught at the University of Utah before settling at UChicago in 1955.
He began studying the temperature of the Sun's corona, and his calculations showed the conditions should produce a supersonic flow of particles off the surface.
The idea was initially met with skepticism -- even ridicule.
- 'Utter nonsense' -
"The first reviewer on the paper said, 'Well, I would suggest that Parker go to the library and read up on the subject before he tries to write a paper about it, because this is utter nonsense,'" Parker told UChicago News in 2018.
His idea only saw publication in the Astrophysical Journal when then editor and future Nobel prize winner Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar realized he could not find a flaw in Parker's math, and overrode the objections of both of the reviewers.
The theory was proved correct in 1962 when NASA's Mariner II spacecraft, which flew to Venus, encountered the stream of particles, called the solar wind.
Scientists now know that solar wind blankets all the planets, protecting them from harmful radiation, but also at times disrupting communications here on Earth when solar flares occur.
Parker also proposed the idea of "nanoflares" -- small solar explosions that occur all over the Sun -- which are responsible for its superheated corona. The corona is hotter than the surface itself, a fact that couldn't be explained by known physics at the time.
He went on to study cosmic rays, the magnetic fields of galaxies and myriad other topics, and won numerous accolades including the US National Medal of Science, the Kyoto Prize, the Crafoord Prize and the American Physical Society Medal for Exceptional Achievement in Research.
"Anyone who knew Dr. Parker, knew that he was a visionary," said Nicola Fox, director of NASA's heliophysics division.
NASA's Parker Solar Probe, named after Parker, was launched in 2018, circling the Sun closer than any spacecraft had previously ventured.
It has already sent back troves of valuable data leading to new discoveries about space weather and the detection of a long theorized zone where the Sun's radiation vaporizes all cosmic dust.
E.AbuRizq--SF-PST




