
-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
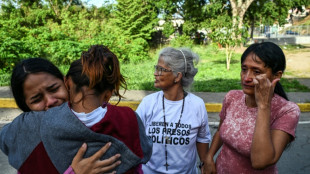
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket

-
 Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
-
Arsenal villain Martinelli turns FA Cup hat-trick hero

-
 Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
-
Kohli hits 93 as India edge New Zealand in ODI opener

-
 Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
-
Toulon win Munster thriller as Quins progress in Champions Cup

-
 NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Leeds rally to avoid FA Cup shock at Derby

-
 Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
-
Liverpool's Bradley out for the season with 'significant' knee injury

-
 Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
-
Comeback kid Hurkacz inspires Poland to first United Cup title

-
 Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
-
Salah and fellow stars aim to deny Morocco as AFCON reaches semi-final stage

-
 Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
-
Iran protest death toll rises as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
-
Venezuelans await release of more political prisoners, Maduro 'doing well'

-
 Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
-
Medvedev warms up in style for Australian Open with Brisbane win

-
 Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
-
Sabalenka fires Australian Open warning with Brisbane domination

-
 In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
-
New protests hit Iran as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
-
Keys draws on happy Adelaide memories before Australian Open defence

-
 Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
-
Ugandan opposition turns national flag into protest symbol

-
 Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
-
'Quad God' Malinin warms up for Olympics with US skating crown


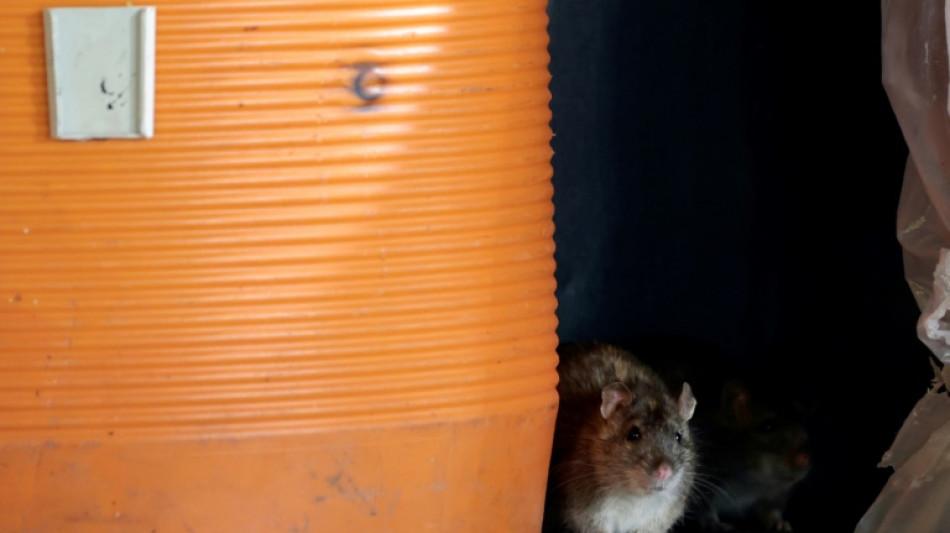
Forget mammoths, study shows how to resurrect Christmas Island rats
Ever since the movie Jurassic Park, the idea of bringing extinct animals back to life has captured the public's imagination -- but what might scientists turn their attention towards first?
Instead of focusing on iconic species like the woolly mammoth or the Tasmanian tiger, a team of paleogeneticists have studied how, using gene editing, they could resurrect the humble Christmas Island rat, which died out around 120 years ago.
Though they did not follow through and create a living specimen, they say their paper, published in Current Biology on Wednesday, demonstrates just how close scientists working on de-extinction projects could actually get using current technology.
"I am not doing de-extinction, but I think it's a really interesting idea, and technically it's really exciting," senior author Tom Gilbert, an evolutionary geneticist at the University of Copenhagen, told AFP.
There are three pathways to bringing back extinct animals: back-breeding related species to achieve lost traits; cloning, which was used to create Dolly the sheep in 1996; and finally genetic editing, which Gilbert and colleagues looked at.
The idea is to take surviving DNA of an extinct species, and compare it to the genome of a closely-related modern species, then use techniques like CRISPR to edit the modern species' genome in the places where it differs.
The edited cells could then be used to create an embryo implanted in a surrogate host.
Gilbert said old DNA was like a book that has gone through a shredder, while the genome of a modern species is like an intact "reference book" that can be used to piece together the fragments of its degraded counterpart.
His interest in Christmas Island rats was piqued when a colleague studied their skins to look for evidence of pathogens that caused their extinction around 1900.
It's thought that black rats brought on European ships wiped out the native species, described in an 1887 entry of the Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London as a "fine new Rat," large in size with a long yellow-tipped tail and small rounded ears.
- Key functions lost -
The team used brown rats, commonly used in lab experiments, as the modern reference species, and found they could reconstruct 95 percent of the Christmas Island rat genome.
That may sound like a big success, but the five percent they couldn't recover was from regions of the genome that controlled smell and immunity, meaning that the recovered rat might look the same but would lack key functionality.
"The take home is, even if we have basically the perfect ancient DNA situation, we've got a really good sample, we've sequenced the hell out of it, we're still lacking five percent of it," said Gilbert.
The two species diverged around 2.6 million years ago: close in evolutionary time, but not close enough to fully reconstruct the lost species' full genome.
This has important implications for de-extinction efforts, such as a project by US bioscience firm Colossal to resurrect the mammoth, which died out around 4,000 years ago.
Mammoths have roughly the same evolutionary distance from modern elephants as brown rats and Christmas Island rats.
Teams in Australia meanwhile are looking at reviving the Tasmanian tiger, or thylacine, whose last surviving member died in captivity in 1936.
Even if gene-editing were perfected, replica animals created with the technique would thus have certain critical deficiencies.
"Let's say you're bringing back a mammoth solely to have a hairy elephant in a zoo to raise money or get conservation awareness -- it doesn't really matter," he said.
But if the goal is to bring back the animal in its exact original form "that's never going to happen," he said.
Gilbert admitted that, while the science was fascinating, he had mixed feelings on de-extinction projects.
"I'm not convinced it is the best use of anyone's money," he said. "If you had to choose between bringing back something or protecting what was left, I'd put my money into protection."
O.Farraj--SF-PST




