
-
 McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
McTominay double gives Napoli precious point at Serie A leaders Inter
-
Trump admin sends more agents to Minneapolis despite furor over woman's killing

-
 Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
Allen magic leads Bills past Jaguars in playoff thriller
-
Barca edge Real Madrid in thrilling Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
Malinin spearheads US Olympic figure skating challenge
-
Malinin spearheads US figure Olympic figure skating challenge

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing', govt calls counter-protests
-
'Fragile' Man Utd hit new low with FA Cup exit

-
 Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
Iran rights group warns of 'mass killing' of protesters
-
Demonstrators in London, Paris, Istanbul back Iran protests

-
 Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
Olise sparkles as Bayern fire eight past Wolfsburg
-
Man Utd knocked out of FA Cup by Brighton, Martinelli hits hat-trick for Arsenal

-
 Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
Troubled Man Utd crash out of FA Cup against Brighton
-
Danish PM says Greenland showdown at 'decisive moment' after new Trump threats

-
 AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
AC Milan snatch late draw at Fiorentina as title rivals Inter face Napoli
-
Venezuelans demand political prisoners' release, Maduro 'doing well'
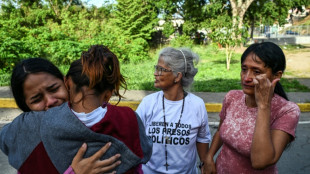
-
 'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
'Avatar: Fire and Ashe' leads in N.America for fourth week
-
Bordeaux-Begles rout Northampton in Champions Cup final rematch

-
 NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will compete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Kohli surpasses Sangakkara as second-highest scorer in international cricket

-
 Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
Young mother seeks five relatives in Venezuela jail
-
Arsenal villain Martinelli turns FA Cup hat-trick hero

-
 Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
Syrians in Kurdish area of Aleppo pick up pieces after clashes
-
Kohli hits 93 as India edge New Zealand in ODI opener

-
 Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
Trump tells Cuba to 'make a deal, before it is too late'
-
Toulon win Munster thriller as Quins progress in Champions Cup

-
 NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
NHL players will complete at Olympics, says international ice hockey chief
-
Leeds rally to avoid FA Cup shock at Derby

-
 Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
Rassat sweeps to slalom victory to take World cup lead
-
Liverpool's Bradley out for the season with 'significant' knee injury

-
 Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
Syria govt forces take control of Aleppo's Kurdish neighbourhoods
-
Comeback kid Hurkacz inspires Poland to first United Cup title

-
 Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
Kyiv shivers without heat, but battles on
-
Salah and fellow stars aim to deny Morocco as AFCON reaches semi-final stage

-
 Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
Mitchell lifts New Zealand to 300-8 in ODI opener against India
-
Iran protest death toll rises as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
Malaysia suspends access to Musk's Grok AI: regulator
-
Venezuelans await release of more political prisoners, Maduro 'doing well'

-
 Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
Kunlavut seals Malaysia Open title after injured Shi retires
-
Medvedev warms up in style for Australian Open with Brisbane win

-
 Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
Bublik powers into top 10 ahead of Australian Open after Hong Kong win
-
Sabalenka fires Australian Open warning with Brisbane domination

-
 In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
In Gaza hospital, patients cling to MSF as Israel orders it out
-
New protests hit Iran as alarm grows over crackdown 'massacre'

-
 Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
Svitolina powers to Auckland title in Australian Open warm-up
-
Keys draws on happy Adelaide memories before Australian Open defence

-
 Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
Scores of homes razed, one dead in Australian bushfires
-
Ugandan opposition turns national flag into protest symbol

-
 Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
Bears banish Packers, Rams survive Panthers playoff scare
-
'Quad God' Malinin warms up for Olympics with US skating crown


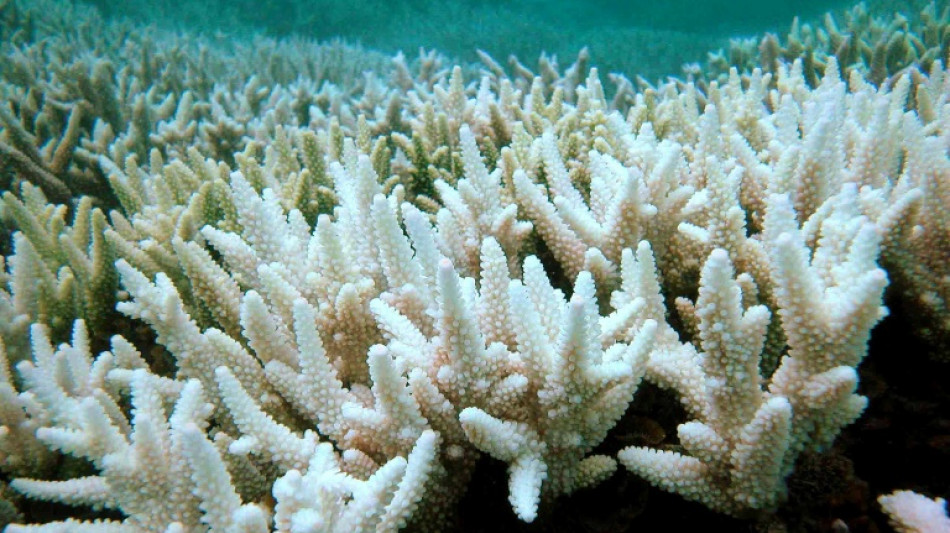
On land and sea, climate change causing 'irreversible' losses: UN
Climate change has already caused "irreversible losses" for Nature, UN experts have said, warning that if emissions are not cut quickly, warming could trigger chain reactions with potentially catastrophic effects for all species, including humans.
All forms of life on Earth are linked together by a vast web of causes and consequences, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) said in a new report on the impacts of global warming published this week.
Those effects are severe and wide ranging across the world's natural habitats.
"Climate change has caused substantial damages, and increasingly irreversible losses, in terrestrial, freshwater and coastal and open marine ecosystems," the IPPC says in its key Summary for Policymakers.
And "unsustainable development" is only increasing the vulnerability to danger.
- 'Tipping point' -
Many natural systems have already reached or are close to the limit of their ability to cope with the effects of a warming planet.
The oceans have absorbed huge quantities of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as emissions have grown, but this has come at the cost of changing the water chemistry -- ocean acidification -- that harms sea life.
Warming is also linked to an increasing number of powerful marine heatwaves that drive harmful algal blooms, kill fish and cause coral bleaching.
Coral reefs are home to at least a quarter of all marine animals and plants.
But battered by repeated marine heatwaves, the world's shallow water corals are "unlikely to last the century", the IPCC said, if global warming continues without a dramatic reduction in emissions.
Forests, tropical or boreal, are also particularly threatened by rising temperatures, drought and fire.
Mortality increases of 20 percent have been recorded for trees in some areas.
At four degrees Celsius of warming, the IPCC report said, half of the Amazon could reach a "tipping point", becoming a savannah and starting to release its vast store of C02, further accelerating warming.
At just 2C, the world's permafrost could begin to thaw, releasing immense quantities of methane, a greenhouse gas much more powerful over the short term than CO2.
While the Paris agreement goal is to limit warming at 1.5C above pre-industrial levels, current international plans and pledges would see temperatures rise up to 2.7C.
- Extinctions -
The Earth is already believed to be entering its sixth mass extinction, driven by humanity's overconsumption and comprehensive destruction of species and habitats.
And global warming is increasingly adding to that threat, with two species -- the Golden Toad of Costa Rica and the Australian rodent Bramble Cays Melomys -- recognised as extinct because of climate change, the IPCC said.
A best case scenario is that nine percent of all the world's species will likely be "at high risk" of extinction with 1.5C of warming, the IPCC said.
At 4C the most pessimistic scenario is 39 percent imperilled.
Even the very lowest estimates are a thousand times higher than the natural rate of extinctions.
- Protection call -
On land or sea, for animal or plant, the threat is everywhere.
But the IPCC said only 15 percent of land, 21 percent of freshwater and eight percent of oceans are protected, throwing its weight behind calls to effectively safeguard 30 to 50 percent of the planet to maintain the "resilience of biodiversity and ecosystem services at a global scale".
That is because protecting nature is a virtuous circle: trees store carbon and provide shade, wetlands reduce flooding and protect coasts from erosion, insects participate in pollination.
Conversely, enabling destruction multiplies the dangers.
"Exploitation of wildlife and degradation of natural habitats have increased opportunities for 'spill over' of pathogens from wildlife to human populations and increased emergence of zoonotic disease epidemics and pandemics," the IPCC notes.
Many of these risks are now unavoidable in the short term, regardless of the trajectory of emissions of greenhouse gases, warns the report.
So the IPCC emphasises the need to fight global warming both by reducing emissions and preparing for its impacts.
And "the best way to achieve this is to let nature do the job," UN Environment Programme chief Inger Andersen told a press conference this week.
"We need large scale ecosystem restoration from ocean to mountain top."
X.AbuJaber--SF-PST




