
-
 New NBA dunk contest champ assured and shooting stars return
New NBA dunk contest champ assured and shooting stars return
-
Shiffrin says will use lessons learnt from Beijing flop at 2026 Games

-
 Takaichi tipped for big win as Japan votes
Takaichi tipped for big win as Japan votes
-
Lens return top of Ligue 1 with win over Rennes

-
 Shiffrin learning from Beijing lessons ahead of Milan-Cortina bow
Shiffrin learning from Beijing lessons ahead of Milan-Cortina bow
-
Demonstrators in Berlin call for fall of Iran's Islamic republic

-
 'Free the mountains!": clashes at Milan protest over Winter Olympics
'Free the mountains!": clashes at Milan protest over Winter Olympics
-
Townsend accepts pressure will mount on him after Italy defeat

-
 BMW iX3 new style and design
BMW iX3 new style and design
-
Suryakumar's 84 leads India to opening win over USA in T20 World Cup

-
 Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Milan-Cortina Games
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Milan-Cortina Games
-
Barca beat Mallorca to extend Liga lead

-
 Gyokeres lifts Arsenal nine clear as Man Utd pile pressure on Frank
Gyokeres lifts Arsenal nine clear as Man Utd pile pressure on Frank
-
Late Guirassy winner for Dortmund trims Bayern's lead atop Bundesliga

-
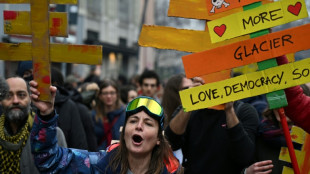 'Free the mountains!": protest in Milan over Winter Olympics
'Free the mountains!": protest in Milan over Winter Olympics
-
Gyokeres double helps Arsenal stretch Premier League lead

-
 New Skoda Epiq: modern with range
New Skoda Epiq: modern with range
-
Six Nations misery for Townsend as Italy beat sorry Scotland

-
 Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain
Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain
-
Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection

-
 Over 2,200 IS detainees transferred to Iraq from Syria: Iraqi official
Over 2,200 IS detainees transferred to Iraq from Syria: Iraqi official
-
Norway's Ruud tops Olympic men's freeski slopestyle qualifying

-
 Czech qualifier Bejlek claims first title in Abu Dhabi
Czech qualifier Bejlek claims first title in Abu Dhabi
-
French duo reach Shanghai, completing year-and-a-half walk

-
 Australian snowboarder James eyes elusive Olympic gold
Australian snowboarder James eyes elusive Olympic gold
-
Sequins and snow: Eva Adamczykova makes Olympic return

-
 Vonn set for Olympic medal bid after successful downhill training
Vonn set for Olympic medal bid after successful downhill training
-
Shepherd takes hat-trick as West Indies beat Scotland in T20 World Cup

-
 Sausages will sell after thrill-seeker Von Allmen wins Olympic downhill
Sausages will sell after thrill-seeker Von Allmen wins Olympic downhill
-
Swiss racer Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics

-
 'Wake up': Mum sparks comeback after scare for freeski star Gu
'Wake up': Mum sparks comeback after scare for freeski star Gu
-
Von Allmen wins men's Olympic downhill gold, first of Games

-
 First medals up for grabs at Winter Olympics
First medals up for grabs at Winter Olympics
-
Afghanistan captain Khan harbours dream of playing in Kabul

-
 Lindsey Vonn completes second Winter Olympics downhill training run
Lindsey Vonn completes second Winter Olympics downhill training run
-
Freeski star Gu survives major scare in Olympic slopestyle

-
 Iran FM looks to more nuclear talks, but warns US
Iran FM looks to more nuclear talks, but warns US
-
Hetmyer's six-hitting steers West Indies to 182-5 against Scotland

-
 After boos for Vance, IOC says it hopes for 'fair play'
After boos for Vance, IOC says it hopes for 'fair play'
-
Thousands gather as Pakistan buries victims of mosque suicide attack

-
 Lindsey Vonn completes second downhill training session
Lindsey Vonn completes second downhill training session
-
US pressing Ukraine and Russia to end war by June, Zelensky says

-
 Faheem blitz sees Pakistan avoid Netherlands shock at T20 World Cup
Faheem blitz sees Pakistan avoid Netherlands shock at T20 World Cup
-
Trump refuses to apologize for racist clip of Obamas as monkeys

-
 Takaichi talks tough on immigration on eve of vote
Takaichi talks tough on immigration on eve of vote
-
England's Salt passed fit for T20 World Cup opener

-
 Spain, Portugal brace for fresh storm after flood deaths
Spain, Portugal brace for fresh storm after flood deaths
-
Pakistan bowl out Netherlands for 147 in T20 World Cup opener

-
 Pushed to margins, women vanish from Bangladesh's political arena
Pushed to margins, women vanish from Bangladesh's political arena
-
Crypto firm accidentally sends $40 bn in bitcoin to users


UN forecasts La Nina could help lower temperatures this year
The return of the cooling La Nina weather phenomenon this year should help lower temperatures somewhat after months of global heat records, the United Nations' weather agency said Monday.
The impact is likely to be felt in the next few months because the warming El Nino weather pattern -- which has helped fuel a spike in global temperatures and extreme weather around the world since mid-2023 -- "is showing signs of ending", the UN's World Meteorological Organization said in its latest update.
The WMO warned, however, that global temperatures would continue to rise in the long term due to human-induced climate change, which continues to make extreme weather worse and upend seasonal rainfall and temperature patterns.
La Nina refers to the cooling of the ocean surface temperatures in large swathes of the tropical Pacific Ocean, coupled with winds, rains and changes in atmospheric pressure.
In many locations, especially in the tropics, La Nina produces the opposite climate impacts to El Nino, which heats up the surface of the oceans, leading to drought in some parts of the world and triggering heavy downpours elsewhere.
The WMO said there was a "60 percent" chance of La Nina conditions in the period from July to September and a "70 percent" likelihood during August-November.
The chances of El Nino redeveloping are negligible, it added.
Every month since June 2023, when El Nino returned, has set a new high temperature record, and 2023 was by far the warmest year on record globally.
The WMO said the planet would continue to heat up overall from the use of fossil fuels that produce greenhouse gases.
- Man-made global heating -
"The end of El Nino does not mean a pause in long-term climate change, as our planet will continue to warm due to heat-trapping greenhouse gases," WMO deputy secretary general Ko Barrett stressed.
"Exceptionally high sea surface temperatures will continue to play an important role during next months."
Much of the planet's excess heat from climate change is stored in the oceans.
In the United States, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has already factored the expected La Nina into its forecasts for this year's Atlantic hurricane season.
The NOAA said it expected four to seven major hurricanes in the Atlantic between June and November.
"The upcoming Atlantic hurricane season is expected to have above-normal activity due to a confluence of factors, including near-record warm ocean temperatures in the Atlantic Ocean, development of La Nina conditions in the Pacific, reduced Atlantic trade winds and less wind shear," the NOAA said on May 23.
The WMO noted that the past nine years had been the warmest on record, even with the cooling influence of a La Nina event that lasted from 2020 to early 2023.
The latest El Nino, which peaked in December, was one of the five strongest on record.
"Our weather will continue to be more extreme because of the extra heat and moisture in our atmosphere," Barrett said.
The WMO has made it a priority to ensure that all regions of the world are covered by early warning systems by 2027, particularly the least well-equipped, such as Africa.
"Seasonal forecasts for El Nino and La Nina, and the anticipated impacts on the climate patterns globally, are an important tool to inform early warnings and early action," Barrett said.
R.Shaban--SF-PST



