
-
 Stocks mostly higher before US-Russia summit
Stocks mostly higher before US-Russia summit
-
Bayern's Bundesliga crown up for grabs after rocky summer

-
 Arsenal face revamped Man Utd as new-look Liverpool open Premier League season
Arsenal face revamped Man Utd as new-look Liverpool open Premier League season
-
South Korea president vows to build 'military trust' with North

-
 'Never again': Indigenous Bolivians sour on socialism
'Never again': Indigenous Bolivians sour on socialism
-
Indonesia's president touts economy, social welfare drive

-
 World plastic pollution treaty talks collapse with no deal
World plastic pollution treaty talks collapse with no deal
-
Facing US tariffs, India's Modi vows self-reliance

-
 Trump to meet Putin in high-stakes Alaska summit
Trump to meet Putin in high-stakes Alaska summit
-
Indian rescuers scour debris after 60 killed in flood

-
 Ivory Coast village reburies relatives as rising sea engulfs cemetery
Ivory Coast village reburies relatives as rising sea engulfs cemetery
-
Stressed UK teens seek influencers' help for exams success

-
 National Guard deploys 800 personnel for DC mission, says Pentagon
National Guard deploys 800 personnel for DC mission, says Pentagon
-
Japan emperor expresses 'deep remorse' 80 years after WWII

-
 With waters at 32C, Mediterranean tropicalisation shifts into high gear
With waters at 32C, Mediterranean tropicalisation shifts into high gear
-
Historic Swedish church being moved as giant mine casts growing shadow

-
 Malawi's restless youth challenged to vote in September polls
Malawi's restless youth challenged to vote in September polls
-
Indonesian roof tilers flex muscles to keep local industry alive

-
 World's first humanoid robot games begin in China
World's first humanoid robot games begin in China
-
Scott Barrett returns to lead All Blacks against Argentina

-
 Five things to know about Nigeria's oil sector
Five things to know about Nigeria's oil sector
-
New compromise but still no deal at plastic pollution talks

-
 France's Cernousek seizes lead at LPGA Portland Classic
France's Cernousek seizes lead at LPGA Portland Classic
-
Putin-Trump summit: What each side wants

-
 Desperate Myanmar villagers scavenge for food as hunger bites
Desperate Myanmar villagers scavenge for food as hunger bites
-
Qualifier Atmane stuns Rune to set up Sinner semi-final in Cincinnati

-
 Hong Kong tycoon Jimmy Lai's security trial delayed over health concerns
Hong Kong tycoon Jimmy Lai's security trial delayed over health concerns
-
Asia stocks mixed before US-Russia summit

-
 Putin hails North Korean troops as 'heroic' in letter to Kim
Putin hails North Korean troops as 'heroic' in letter to Kim
-
Fleeing the heat, tourists explore Rome at night, underground

-
 Online cockfighting thrives in Philippines despite ban and murders
Online cockfighting thrives in Philippines despite ban and murders
-
Keeping cool with colours -- Vienna museum paints asphalt to fight heat

-
 Raising the bar: Nepal's emerging cocktail culture
Raising the bar: Nepal's emerging cocktail culture
-
El Salvador plans 600 mass trials for suspected gang members

-
 Trump's tariffs drown Brazil's fish industry
Trump's tariffs drown Brazil's fish industry
-
Hong Kong tycoon Jimmy Lai's collusion trial resumes after delay

-
 Britain's Princess Anne turns 75 with typically minimal fuss
Britain's Princess Anne turns 75 with typically minimal fuss
-
Japan posts modest growth despite US tariffs

-
 Rugby Championship kicks off amid uncertain future
Rugby Championship kicks off amid uncertain future
-
Israeli far-right minister backs contentious West Bank settlement plan

-
 Hot putter carries MacIntyre to three-shot lead at BMW Championship
Hot putter carries MacIntyre to three-shot lead at BMW Championship
-
'Ridiculous': How Washington residents view the new troops in town

-
 Global plastic pollution treaty talks extended in 'haze' of confusion
Global plastic pollution treaty talks extended in 'haze' of confusion
-
Trump's tariffs have not reduced Panama Canal traffic -- yet

-
 YouTube turns to AI to spot children posing as adults
YouTube turns to AI to spot children posing as adults
-
Sky's the limit for Duplantis ahead of 'super-sick' Tokyo worlds

-
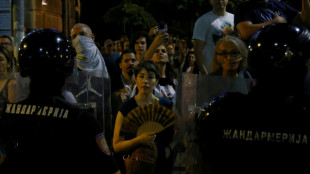 New clashes in Serbia as political crisis escalates
New clashes in Serbia as political crisis escalates
-
Sinner swamps Auger-Aliassime in Cincinnati power display

-
 Oil prices rise ahead of US-Russia summit as stocks digest inflation data
Oil prices rise ahead of US-Russia summit as stocks digest inflation data
-
California to change election maps to counter Texas, governor says


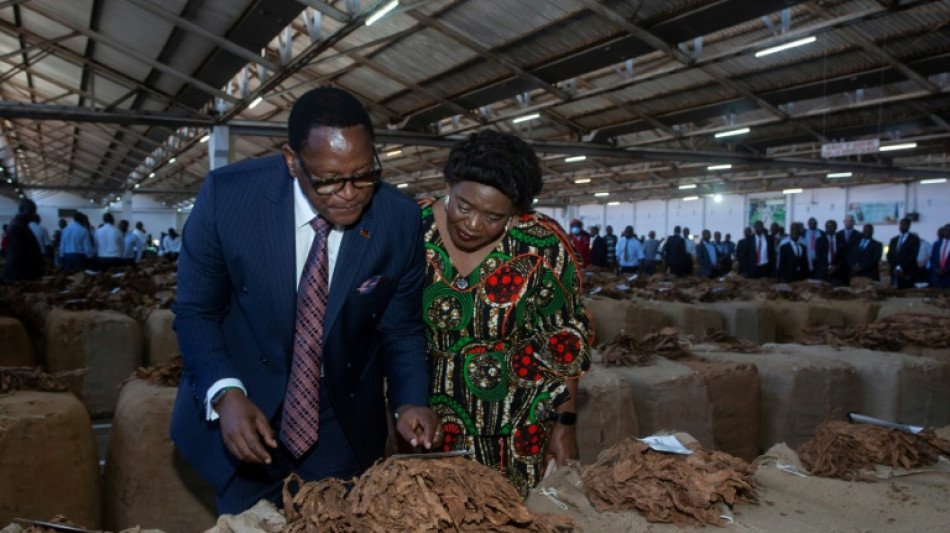
Malawi's debt crisis deepens as aid cuts hurt
Behind a dimly lit bar in Malawi's capital, Ben Manda rubbed his tired eyes and poured a customer a drink. He had been working for 36 hours straight, packing in back-to-back shifts to feed his family of four.
"I haven't been home in three days," said the 32-year-old barman in a run-down club in Mtandire, one of Lilongwe's largest and most crowded informal settlements. "Times are tough."
Manda is a casualty of Malawi's economic struggles, his livelihood hanging by a thread as foreign aid cuts and mounting national debt tighten their grip on his destitute African country.
A small television above the bar flickered with news reports of budget shortfalls, unpaid salaries, and a spiralling cost of living.
"The problem is that our leaders divert the money from its intended use," Manda said, accusing the political leadership of misusing foreign aid.
The country of 21 million people -- more than two-thirds of whom live in extreme poverty, according to the World Bank -- has for decades been dependent on foreign aid.
The scaling back of funding from Washington's USAID agency this year as well as cuts by Britain and other donors has fed a storm of crises causing economic instability that is worsening ahead of general elections in September.
"Since 2013, the country has lost an estimated five percent of its GDP, or roughly $545 million annually, due to reduced donor assistance," Agness Nyirongo, economic governance officer for the Centre for Social Concern, a non-government organisation, told AFP.
"The aid withdrawal means the country has to prioritise the little revenue locally generated to repay loans at the expense of service delivery," said Willy Kambwandira of the Centre for Social Accountability and Transparency.
Malawi is one of six countries with unsustainable debt levels, according to the International Monetary Fund's (IMF) February 2025 list.
Public sector debt rose from 48 to 93 percent of GDP between March 2020 and March 2024, according to government figures cited in an IMF report this month.
"Fiscal pressures that have contributed to this rise include spending to combat the Covid-19 pandemic and the aftereffects of three cyclones, high inflation, and rising foreign exchange rates," it said.
- Little left over -
Structural weaknesses and fiscal mismanagement have contributed to Malawi's economic woes, said university lecturer Bertha Chikadza, president of the Economics Association of Malawi.
For example, tobacco dominates exports, making up 60 percent, and price slumps for the crop have cut foreign exchange earnings.
"With little or no diversification in export earnings, the country has had persistent trade deficits," she said.
Debt servicing consumes about half of domestic revenue, leaving little for health, education and other critical sectors, Chikadza said.
With inflation of 28.5 percent this year pushing up prices, Malawians have taken to the streets in protest in several cities.
Government coping measures, including cutting public spending and raising taxes, have been deeply unpopular.
President Lazarus Chakwera, standing for re-election in September, repeated at the UN General Assembly last year pleas for debt relief to give his country -- and African nations in a similar plight -- some "breathing space".
The topic is a priority this year for the G20 group of leading economies under the presidency of South Africa, the first African nation to hold the role.
More than half of Africa's 1.3 billion people live in countries that spend more on interest payments than on social issues such as health, education and infrastructure, according to the South African government.
The solution is not to write off debt, said David McNair, global policy executive director at the One Campaign non-profit group.
Developing countries such as Malawi "need more borrowing to allow them to invest, particularly because of the demographic trends," he said.
However, their debt is "too expensive," he said, calling for the G20 to put in place a review of ratings agencies' assessments of debt risk and find ways to unlock lower-cost private capital.
Q.Najjar--SF-PST
