
-
 Almeida wins time-trial to take Tour of Switzerland
Almeida wins time-trial to take Tour of Switzerland
-
Bublik sees off Medvedev to claim second title on grass in Halle

-
 Feyi-Waboso banned for England tour to Argentina
Feyi-Waboso banned for England tour to Argentina
-
US strikes on Iran: what we know

-
 Alcaraz crowned king of Queen's for second time
Alcaraz crowned king of Queen's for second time
-
US says strikes 'devastated' Iran's nuclear program

-
 Bublik sees off Medvedev to claim fifth AFP title in Halle
Bublik sees off Medvedev to claim fifth AFP title in Halle
-
Freed Belarus opposition figure urges Trump to help release all prisoners

-
 Wave of syringe attacks mar France's street music festival
Wave of syringe attacks mar France's street music festival
-
US intervention 'devastated' Iran's nuclear programme says Pentagon

-
 Marc Marquez completes perfect Mugello weekend with Italian MotoGP triumph
Marc Marquez completes perfect Mugello weekend with Italian MotoGP triumph
-
Vondrousova warms up for Wimbledon with Berlin title

-
 India still on top in first Test despite Brook fifty for England
India still on top in first Test despite Brook fifty for England
-
Ukraine army chief vows to expand strikes on Russia

-
 United behind Iran war effort, Israelis express relief at US bombing
United behind Iran war effort, Israelis express relief at US bombing
-
Former England fast bowler David Lawrence dead at 61

-
 At least three impacts in Israel during Iran missile attacks, 23 hurt
At least three impacts in Israel during Iran missile attacks, 23 hurt
-
Trump says US strikes 'obliterated' Iran nuclear sites

-
 Japan's high-tech sunscreens tap into skincare craze
Japan's high-tech sunscreens tap into skincare craze
-
Tesla expected to launch long-discussed robotaxi service

-
 South Korea counts on shipbuilding to ease US tariff woes
South Korea counts on shipbuilding to ease US tariff woes
-
Bombing Iran, Trump gambles on force over diplomacy

-
 Trump says US attack 'obliterated' Iran nuclear sites
Trump says US attack 'obliterated' Iran nuclear sites
-
Itoje to Valetini: five to watch when the Lions face Australia

-
 Wallabies confident but wary of wounded British and irish Lions
Wallabies confident but wary of wounded British and irish Lions
-
Utopia and fragile democracy at Art Basel fair

-
 Freed Israeli hostage recounts 484-day nightmare in Gaza
Freed Israeli hostage recounts 484-day nightmare in Gaza
-
River Plate frustrated by Monterrey in 0-0 stalemate

-
 Panama cuts internet, cell phones in restive province
Panama cuts internet, cell phones in restive province
-
Tens of thousands join pro-Palestinian marches across Europe

-
 Coach Penney unsure of return to Super Rugby champions Crusaders
Coach Penney unsure of return to Super Rugby champions Crusaders
-
Trump says US 'obliterated' Iran nuclear sites, threatens more

-
 Olympic chief Kirsty Coventry's steeliness honed by hard knocks
Olympic chief Kirsty Coventry's steeliness honed by hard knocks
-
Outgoing IOC president Thomas Bach faced mammoth challenges

-
 Maro Itoje comes of age with Lions captaincy
Maro Itoje comes of age with Lions captaincy
-
Trump says US bombs Iran nuclear sites, joining Israeli campaign

-
 In New York, Vermeer show reveals art of the love letter
In New York, Vermeer show reveals art of the love letter
-
Ex-members of secret US abortion group fear return to dark era
-
 Trump says US launched 'very successful' attack on Iran nuclear sites
Trump says US launched 'very successful' attack on Iran nuclear sites
-
Man City squad must be trimmed: Guardiola

-
 Minjee Lee grabs four-shot lead at 'brutal' Women's PGA Championship
Minjee Lee grabs four-shot lead at 'brutal' Women's PGA Championship
-
Olympic balloon rises again in Paris

-
 Inter Milan, Dortmund claim first wins at Club World Cup
Inter Milan, Dortmund claim first wins at Club World Cup
-
South American teams lay down the gauntlet to Europe at Club World Cup

-
 Fleetwood grabs PGA Travelers lead as top-ranked stars fade
Fleetwood grabs PGA Travelers lead as top-ranked stars fade
-
'Lucky' Lamothe hat-trick guides Bordeaux-Begles into Top 14 final

-
 Lamothe hat-trick guides Bordeaux-Begles into Top 14 final
Lamothe hat-trick guides Bordeaux-Begles into Top 14 final
-
UK PM Starmer says Kneecap should not perform Glastonbury

-
 Inter Milan strike late to beat Urawa Reds at Club World Cup
Inter Milan strike late to beat Urawa Reds at Club World Cup
-
Dortmund stars hide from sun at Club World Cup 'sauna'


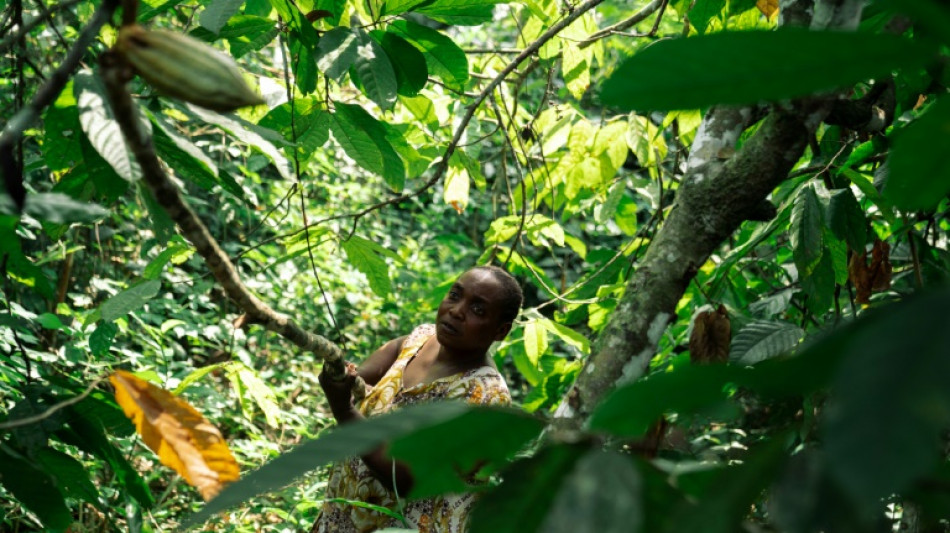
Armed groups covet cocoa in eastern DR Congo
Despite the risks from deadly armed groups roaming the countryside, Judith Kahindo walks alone every day to her isolated cocoa plantation in the war-torn North Kivu region of the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo.
North Kivu is primarily rich in coltan and other minerals that have fuelled the fighting that has ravaged the region for the last three decades.
Vast areas have been seized by the M23 rebel group in a lightning offensive since January including the capital Goma.
But further north in Beni, cocoa, whose prices have soared on the world market in the last two years, also stokes the violence.
Massacres committed by the Allied Democratic Forces (ADF) rebels, who have pledged allegiance to the Islamic State group, have left thousands dead and prevented cocoa farmers from accessing their plantations for years.
"We tend our fields with the fear of being massacred because cocoa is so coveted, whether by the rebels or even our soldiers," said Kahindo, a widow with eight children, as she hacked her way through a tangled forest with a machete.
Cocoa production across the DRC remains relatively marginal, just over one percent of global production.
- Smuggling -
But that is still enough to attract the attention of various armed groups in Beni who fuel smuggling networks to neighbouring Uganda, according to those involved in the sector.
"If there wasn't cocoa in abundance in Beni, the war would already have finished," said Kahindo.
The ADF are not the only threat to people in the area.
"There are people who are taking advantage of the terror caused by the ADF to steal," said Colonel Mak Hazukay, the Congolese army spokesman in the area.
Even before the emergence of the ADF in the 2000s, the region was already plagued by attacks from the "sangabalende" –- criminal groups that specialised in cocoa theft and smuggling, said Richard Kirumba, Beni civil society president.
Kirumba also said that some Congolese soldiers deployed to protect people from the ADF actually tax cocoa traders or loot abandoned fields.
Stolen cocoa is often trafficked through cross-border smuggling networks.
"The criminals sell the cocoa as it is. They just cut it, remove the husks that protect the beans and then sell it directly," said Frank Ndinyoka Kabeya, a cocoa buyer and a member of the Union of Traders of Agricultural Products in Congo.
Unwary buyers risk being stopped by police. But checks are lax in a country where corruption is endemic, according to NGO Transparency International.
On Beni's streets cocoa beans heaped on tarpaulins can be seen drying in the sun and are mainly sold to "small buyers", circumventing certification processes, said Karim Sibenda, an agricultural engineer at a local chocolate factory.
- Organic -
At the National Office of Agricultural Products of Congo (ONAPAC), which is responsible for certifying the quality and origin of cocoa for export, there is a buzz of activity during the harvest season.
Tonnes of beans with a vinegary scent are piled up in the warehouse, where employees fill and stamp canvas bags destined for export.
Company employee Agee Mbughavinywa, who buys and certifies agricultural products, said cocoa producers are identified by a code to ensure traceability.
The bags of cocoa beans are then mainly exported to Uganda, like other agricultural goods in the region.
Since the end of 2021, the DRC authorised Ugandan troops to operate in the region and fight the ADF alongside the Congolese army.
Their presence has been vital in securing vital trade routes and increase exports, ONACAP said.
But this rapprochement between Kinshasa and Kampala has sparked fears in the cocoa market.
"Ugandan buyers are destabilising the sector, they come with cash in hand and impose their prices on producers," said ONACAP's Beni director.
"They don't look at the quality, they take everything and export it under a Ugandan label, this is hampering the country's economy," she said.
In Beni, traditional farming methods and particularly fertile soil allow for the production of organic cocoa.
But the violence is also threatening its organic status. The European Union recently threatened to no longer recognise the label on local products, as insecurity prevents certification by inspectors.
Industry stakeholders fear that could encourage fraudulent exports of Congolese cocoa as Ugandan.
M.AbuKhalil--SF-PST

